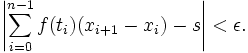In philosophy, systems theory and the sciences,
emergence refers to the way complex systems and patterns, such as those that form a hurricane, arise out of a multiplicity of relatively simple interactions. Like intelligence in the field of AI, or agents in distributed artificial intelligence, emergence is central to the physics of
complex systems and yet very controversial.
"Perhaps the most elaborate recent definition of emergence was provided by Jeffrey Goldstein in the inaugural issue of Emergence.(Goldstein 1999) To Goldstein, emergence refers to "the arising of novel and coherent structures, patterns and properties during the process of self-organization in complex systems." The common characteristics are: (1) radical novelty (features not previously observed in systems); (2) coherence or correlation (meaning integrated wholes that maintain themselves over some period of time); (3) A global or macro "level" (i.e. there is some property of "wholeness"); (4) it is the product of a dynamical process (it evolves); and (5) it is "ostensive" - it can be perceived. For good measure, Goldstein throws in
supervenience -- downward causation." (
Corning 2002)
The term "emergent" was coined by the pioneer psychologist
G. H. Lewes who wrote:
"Every resultant is either a sum or a difference of the co-operant forces; their sum, when their directions are the same -- their difference, when their directions are contrary. Further, every resultant is clearly traceable in its components, because these are homogeneous and commensurable. It is otherwise with emergents, when, instead of adding measurable motion to measurable motion, or things of one kind to other individuals of their kind, there is a co-operation of things of unlike kinds. The emergent is unlike its components insofar as these are incommensurable, and it cannot be reduced to their sum or their difference." (Lewes 1875, p. 412)(Blitz 1992)
However, the concept behind the term has been in use since at least the time of Aristotle.[1] John Stuart Mill[2] and Julian Huxley[3] are just some of the historic luminaries who have written on the concept.

 painless-conjugate-gradient.pdf
painless-conjugate-gradient.pdf