preprocessor
http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/preprocessor.htmlhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C_preprocessorThe preprocessor handles directives for
source file inclusion (
#include),
macro definitions (
#define), and conditional inclusion (
#if).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Preprocessorconstants
macros
include files
#define statementA preprocessor directive terminates at the end-of-line.
A line may be continued by putting a backslash (\) at the end.
(142쪽)
It is common programming practice to use all uppercase letters for macro names. (142쪽)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bourne_shellhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ALGOL_68144쪽
예제 4: first.c
터미널에서 "cc -E main.cpp"라고 치니... @_@
999:~/cintro/ch10/eg4 lym$ cc -E main.cpp
# 1 "main.cpp"
# 1 "<built-in>"
# 1 "<command line>"
# 1 "main.cpp"
# 1 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 1 3 4
# 64 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/_types.h" 1 3 4
# 27 "/usr/include/_types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/sys/_types.h" 1 3 4
# 26 "/usr/include/sys/_types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 1 3 4
# 27 "/usr/include/sys/_types.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/machine/_types.h" 1 3 4
# 26 "/usr/include/machine/_types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/ppc/_types.h" 1 3 4
# 31 "/usr/include/ppc/_types.h" 3 4
typedef signed char __int8_t;
typedef unsigned char __uint8_t;
typedef short __int16_t;
typedef unsigned short __uint16_t;
typedef int __int32_t;
typedef unsigned int __uint32_t;
typedef long long __int64_t;
typedef unsigned long long __uint64_t;
typedef long __darwin_intptr_t;
typedef unsigned int __darwin_natural_t;
# 64 "/usr/include/ppc/_types.h" 3 4
typedef int __darwin_ct_rune_t;
typedef union {
char __mbstate8[128];
long long _mbstateL;
} __mbstate_t;
typedef __mbstate_t __darwin_mbstate_t;
typedef int __darwin_ptrdiff_t;
typedef long unsigned int __darwin_size_t;
typedef __builtin_va_list __darwin_va_list;
typedef int __darwin_wchar_t;
typedef __darwin_wchar_t __darwin_rune_t;
typedef int __darwin_wint_t;
typedef unsigned long __darwin_clock_t;
typedef __uint32_t __darwin_socklen_t;
typedef long __darwin_ssize_t;
typedef long __darwin_time_t;
# 27 "/usr/include/machine/_types.h" 2 3 4
# 28 "/usr/include/sys/_types.h" 2 3 4
struct mcontext;
struct mcontext64;
# 60 "/usr/include/sys/_types.h" 3 4
struct __darwin_pthread_handler_rec
{
void (*__routine)(void *);
void *__arg;
struct __darwin_pthread_handler_rec *__next;
};
struct _opaque_pthread_attr_t { long __sig; char __opaque[36]; };
struct _opaque_pthread_cond_t { long __sig; char __opaque[24]; };
struct _opaque_pthread_condattr_t { long __sig; char __opaque[4]; };
struct _opaque_pthread_mutex_t { long __sig; char __opaque[40]; };
struct _opaque_pthread_mutexattr_t { long __sig; char __opaque[8]; };
struct _opaque_pthread_once_t { long __sig; char __opaque[4]; };
struct _opaque_pthread_rwlock_t { long __sig; char __opaque[124]; };
struct _opaque_pthread_rwlockattr_t { long __sig; char __opaque[12]; };
struct _opaque_pthread_t { long __sig; struct __darwin_pthread_handler_rec *__cleanup_stack; char __opaque[596]; };
# 96 "/usr/include/sys/_types.h" 3 4
typedef __int64_t __darwin_blkcnt_t;
typedef __int32_t __darwin_blksize_t;
typedef __int32_t __darwin_dev_t;
typedef unsigned int __darwin_fsblkcnt_t;
typedef unsigned int __darwin_fsfilcnt_t;
typedef __uint32_t __darwin_gid_t;
typedef __uint32_t __darwin_id_t;
typedef __uint32_t __darwin_ino_t;
typedef __darwin_natural_t __darwin_mach_port_name_t;
typedef __darwin_mach_port_name_t __darwin_mach_port_t;
typedef struct mcontext *__darwin_mcontext_t;
typedef struct mcontext64 *__darwin_mcontext64_t;
typedef __uint16_t __darwin_mode_t;
typedef __int64_t __darwin_off_t;
typedef __int32_t __darwin_pid_t;
typedef struct _opaque_pthread_attr_t
__darwin_pthread_attr_t;
typedef struct _opaque_pthread_cond_t
__darwin_pthread_cond_t;
typedef struct _opaque_pthread_condattr_t
__darwin_pthread_condattr_t;
typedef unsigned long __darwin_pthread_key_t;
typedef struct _opaque_pthread_mutex_t
__darwin_pthread_mutex_t;
typedef struct _opaque_pthread_mutexattr_t
__darwin_pthread_mutexattr_t;
typedef struct _opaque_pthread_once_t
__darwin_pthread_once_t;
typedef struct _opaque_pthread_rwlock_t
__darwin_pthread_rwlock_t;
typedef struct _opaque_pthread_rwlockattr_t
__darwin_pthread_rwlockattr_t;
typedef struct _opaque_pthread_t
*__darwin_pthread_t;
typedef __uint32_t __darwin_sigset_t;
typedef __int32_t __darwin_suseconds_t;
typedef __uint32_t __darwin_uid_t;
typedef __uint32_t __darwin_useconds_t;
typedef unsigned char __darwin_uuid_t[16];
struct sigaltstack
{
void *ss_sp;
__darwin_size_t ss_size;
int ss_flags;
};
typedef struct sigaltstack __darwin_stack_t;
struct ucontext
{
int uc_onstack;
__darwin_sigset_t uc_sigmask;
__darwin_stack_t uc_stack;
struct ucontext *uc_link;
__darwin_size_t uc_mcsize;
__darwin_mcontext_t uc_mcontext;
};
typedef struct ucontext __darwin_ucontext_t;
struct ucontext64 {
int uc_onstack;
__darwin_sigset_t uc_sigmask;
__darwin_stack_t uc_stack;
struct ucontext64 *uc_link;
__darwin_size_t uc_mcsize;
__darwin_mcontext64_t uc_mcontext64;
};
typedef struct ucontext64 __darwin_ucontext64_t;
# 28 "/usr/include/_types.h" 2 3 4
typedef int __darwin_nl_item;
typedef int __darwin_wctrans_t;
typedef unsigned long __darwin_wctype_t;
# 65 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
typedef __darwin_va_list va_list;
typedef __darwin_size_t size_t;
typedef __darwin_off_t fpos_t;
# 98 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
struct __sbuf {
unsigned char *_base;
int _size;
};
struct __sFILEX;
# 132 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
typedef struct __sFILE {
unsigned char *_p;
int _r;
int _w;
short _flags;
short _file;
struct __sbuf _bf;
int _lbfsize;
void *_cookie;
int (*_close)(void *);
int (*_read) (void *, char *, int);
fpos_t (*_seek) (void *, fpos_t, int);
int (*_write)(void *, const char *, int);
struct __sbuf _ub;
struct __sFILEX *_extra;
int _ur;
unsigned char _ubuf[3];
unsigned char _nbuf[1];
struct __sbuf _lb;
int _blksize;
fpos_t _offset;
} FILE;
extern "C" {
extern FILE __sF[];
}
# 248 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern "C" {
void clearerr(FILE *);
int fclose(FILE *);
int feof(FILE *);
int ferror(FILE *);
int fflush(FILE *);
int fgetc(FILE *);
int fgetpos(FILE * , fpos_t *);
char *fgets(char * , int, FILE *);
FILE *fopen(const char * , const char * );
int fprintf(FILE * , const char * , ...) __asm("_" "fprintf" "$LDBLStub");
int fputc(int, FILE *);
int fputs(const char * , FILE * );
size_t fread(void * , size_t, size_t, FILE * );
FILE *freopen(const char * , const char * ,
FILE * ) ;
int fscanf(FILE * , const char * , ...) __asm("_" "fscanf" "$LDBLStub");
int fseek(FILE *, long, int);
int fsetpos(FILE *, const fpos_t *);
long ftell(FILE *);
size_t fwrite(const void * , size_t, size_t, FILE * ) ;
int getc(FILE *);
int getchar(void);
char *gets(char *);
extern const int sys_nerr;
extern const char *const sys_errlist[];
void perror(const char *);
int printf(const char * , ...) __asm("_" "printf" "$LDBLStub");
int putc(int, FILE *);
int putchar(int);
int puts(const char *);
int remove(const char *);
int rename (const char *, const char *);
void rewind(FILE *);
int scanf(const char * , ...) __asm("_" "scanf" "$LDBLStub");
void setbuf(FILE * , char * );
int setvbuf(FILE * , char * , int, size_t);
int sprintf(char * , const char * , ...) __asm("_" "sprintf" "$LDBLStub");
int sscanf(const char * , const char * , ...) __asm("_" "sscanf" "$LDBLStub");
FILE *tmpfile(void);
char *tmpnam(char *);
int ungetc(int, FILE *);
int vfprintf(FILE * , const char * , va_list) __asm("_" "vfprintf" "$LDBLStub");
int vprintf(const char * , va_list) __asm("_" "vprintf" "$LDBLStub");
int vsprintf(char * , const char * , va_list) __asm("_" "vsprintf" "$LDBLStub");
int asprintf(char **, const char *, ...) __asm("_" "asprintf" "$LDBLStub");
int vasprintf(char **, const char *, va_list) __asm("_" "vasprintf" "$LDBLStub");
}
# 308 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern "C" {
char *ctermid(char *);
char *ctermid_r(char *);
FILE *fdopen(int, const char *);
char *fgetln(FILE *, size_t *);
int fileno(FILE *);
void flockfile(FILE *);
const char
*fmtcheck(const char *, const char *);
int fpurge(FILE *);
int fseeko(FILE *, fpos_t, int);
fpos_t ftello(FILE *);
int ftrylockfile(FILE *);
void funlockfile(FILE *);
int getc_unlocked(FILE *);
int getchar_unlocked(void);
int getw(FILE *);
int pclose(FILE *);
FILE *popen(const char *, const char *);
int putc_unlocked(int, FILE *);
int putchar_unlocked(int);
int putw(int, FILE *);
void setbuffer(FILE *, char *, int);
int setlinebuf(FILE *);
int snprintf(char * , size_t, const char * , ...) __asm("_" "snprintf" "$LDBLStub");
char *tempnam(const char *, const char *);
int vfscanf(FILE * , const char * , va_list) __asm("_" "vfscanf" "$LDBLStub");
int vscanf(const char * , va_list) __asm("_" "vscanf" "$LDBLStub");
int vsnprintf(char * , size_t, const char * , va_list) __asm("_" "vsnprintf" "$LDBLStub");
int vsscanf(const char * , const char * , va_list) __asm("_" "vsscanf" "$LDBLStub");
FILE *zopen(const char *, const char *, int);
}
extern "C" {
FILE *funopen(const void *,
int (*)(void *, char *, int),
int (*)(void *, const char *, int),
fpos_t (*)(void *, fpos_t, int),
int (*)(void *));
}
# 372 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern "C" {
int __srget(FILE *);
int __svfscanf(FILE *, const char *, va_list) __asm("_" "__svfscanf" "$LDBLStub");
int __swbuf(int, FILE *);
}
static inline int __sputc(int _c, FILE *_p) {
if (--_p->_w >= 0 || (_p->_w >= _p->_lbfsize && (char)_c != '\n'))
return (*_p->_p++ = _c);
else
return (__swbuf(_c, _p));
}
# 2 "main.cpp" 2
int main() {
printf("The square of all the parts is %d\n",
7 + 5 * 7 + 5);
return(0);
}
예제5: max.c
int main()
{
int counter;
for (counter = =10; counter > 0; --counter)
printf("Hi there\n");
return(0);
}
예제6: size.c
int main()
{
int size;
size = 10; -2;;
printf("Size is %d\n", size);
return(0);
}
예제7: die.c
int main()
{
int value;
value = 1;
if (value < 0)
fprintf((&__sF[2]), "Fatal Error:Abort\n");exit(8);;
printf("We did not die\n");
return (0);
}
#define vs. constconst
http://www.cprogramming.com/tutorial/const_correctness.html
The const keyword allows you to specify whether or not a variable is
modifiable. You can use const to prevent modifications to variables and const
pointers and const references prevent changing the data pointed to (or
referenced).
Conditional Compilationhttp://cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/preprocessor.html#ifdef
allows a section of a program to be compiled only if the macro that is
specified as the parameter has been defined, no matter which its value
is.
#endif
the whole structure of
#if,
#elif and
#else chained directives ends with
#endif.
#undef
#ifndef
#ifndef symbol is true if the symbol is not defined.
#else
http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/C_Programming/Preprocessorinclude FilesFiles that are included in other programs are called header files.
The
angle brackets (<>) indicate that the file is a standard header
file. (On UNIX, these files are located in /usr/include.)
Standard include files define data structures and macros used by library routines. (eg.
printf is a library routine that prints data on the standard output. The
FILE structure used by
printf and its related routines is defined in
stdio.h.)
cstdio (stdio.h)
C library to perform Input/Output operations
http://cplusplus.com/reference/clibrary/cstdio/
This library uses what are called streams to operate with
physical devices such as keyboards, printers, terminals or with any
other type of files supported by the system. Streams are an abstraction
to interact with these in an uniform way; All streams have similar
properties independently of the individual characteristics of the
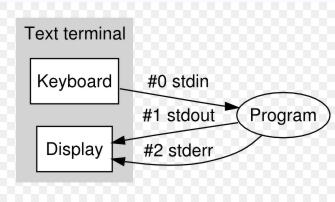
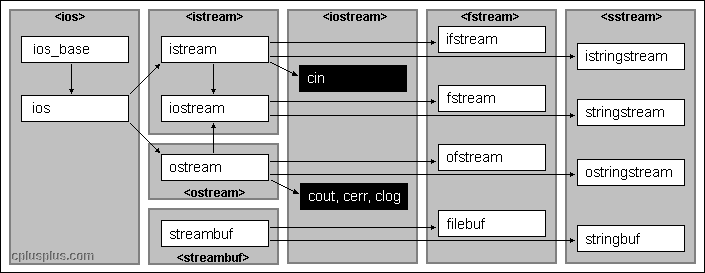
physical media they are associated with.Streams are handled in the cstdio library as pointers to FILE objects. A pointer to a FILE object uniquely identifies a stream, and is used as a parameter in the operations involving that stream.
There also exist three standard streams: stdin, stdout and stderr, which are automatically created and opened for all programs using the library.
Local
include files are particulary useful for storing constants and data
structures when a program spans several files. (149쪽) Local include
files may be specified by using double quotes (" ") around the file
name. The specification can be a simple file, a relative path, or an
absolute path.
그니까 148쪽 symbol은 뭐고 149쪽 union이 뭐냐고???

 invalid-file
invalid-file