2006. 5. 1. 16:20
Computation/Language
* Object-Oriented Programming Concepts
object-oriented design
: A software design method that models the characteristics of abstract or real objects using classes and objects.
Object
: a software bundle of related variables and methods. (Software objects are often used to model real-world objects you find in everyday life.)
A software object can represent real-world objects and abstract concepts like an event.
> what the software object knows is 'state' and what it can do is 'behavior'.
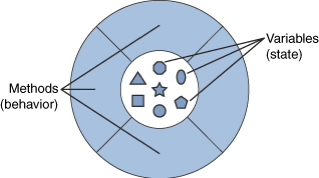
variable
: an item of data named by an identifier. Each variable has a type, such as int or Object, and a scope
컴퓨터 프로그래밍 언어에서의 변수의 의미는, 컴퓨터 기억 장소를 가리키는 추상적인 표현방법입니다. 즉, 기억 장소의 주소를 상징화한 것입니다. 변수에 대한 정의가 아직까지 정확하게 이해되지 않는 분들이 많으시리라 생각됩니다.
다른 예에 빗대자면 이렇습니다. '동경 135˚, 북위 37.5˚'가 메모리 주소라면, '한국(Korea)'은 이를 나타내는 변수(정확히 변수의 이름)가 되는 것입니다.
변수는 다음과 같은 속성을 가지고 있습니다.
이름(Name)
변수의 호칭입니다.
주소(Address)
변수와 연결되는 메모리의 위치를 말합니다. 이 때, 변수가 나타내는 메모리 위치는 항상 동일하지 않습니다. 즉, 동일한 이름을 가진 변수라도 이 변수가 각기 다른 용도로 쓰일 때에는 서로 독립적인 개체로 보고, 이들 변수가 가리키는 주소도 서로 다르게 됩니다. 변수의 주소를 가끔 'l-value'라고도 하는데, 이는 할당문에서 변수가 좌변에 위치한다는 사실에 기인한 것입니다.
값(Value)
변수의 값은 변수와 연결된 메모리 위치에 담겨 있는 내용을 말합니다. 'Apple'이라는 이름을 가진 변수의 메모리 주소가 '00DE'이고, 이 공간에 저장된 내용이 실수 '3.41'라고 하면, 이것이 바로 변수의 값이 되는 것입니다. 변수의 값을 가리켜 'r-value'라고도 합니다.
자료형(Type)
변수의 자료형은 변수가 가질 수 있는 값의 범위와 적용 가능한 연산자의 집합을 결정합니다. 예를 들어, C 언어에서 'int' 자료형은 -32768~32767 까지의 범위에 해당하는 값을 가질 수 있으며, 사칙연산 및 라이브러리 함수로 제공되는 연산자를 사용할 수 있습니다.
scope
:
class variable
: A data item associated with a particular class as a whole--not with particular instances of the class. Class variables are defined in class definitions. = static field
instance variable
: Any item of data that is associated with a particular object. Each instance of a class has its own copy of the instance variables defined in the class.
field
: A data member of a class. Unless specified otherwise, a field is not static.
- 수명에 따라
정적 변수(Static Variable)
스택 기반 동적 변수(Stack-Dynamic Variable)
명시적 힙 기반 동적 변수(Explicit Heap-Dynamic Variable)
묵시적 동적 변수(Implicit Dynamic Variable)
- 실효 범위(:변수의 값을 참조할 수 있는 범위, 즉 변수가 사용되는 문장의 범위)에 따라
local variable
: A data item known within a block, but inaccessible to code outside the block. For example, any variable defined within a method is a local variable and can't be used outside the method.
지역 변수는 변수가 선언된 프로그램 단일체나 함수 혹은 블록 안에서만 사용할 수 있는 변수
cf. 스택 기반 동적 변수(Static Dynamic Variable)는 선언문이 실행될 때 저장 장소 바인딩이 이루어지고, 그에 대한 자료형은 정적으로 바인딩 됩니다. 다시 말해서, 변수가 프로그램 시작 시에 바인딩 되는 것이 아니라, 프로그램을 한 줄 한 줄 수행하고 있는 동안, 변수를 선언하는 코드 부분이 나오면 그제서야 변수에 대한 저장 장소가 할당되고, 바인딩이 이루어지는 것입니다. 이러한 함수에서 선언되는 변수들을 지역 변수(Local Variable)라고 하는데, 지역 변수들에 대한 기억 장소가 바로 이 때 할당되며 함수의 수행이 모두 끝나면 반환됩니다.
non-local variable
: 비지역 변수는 전체 프로그램에 걸쳐 사용 가능한 변수를 말합니다.
pointer variable
: 포인터 변수는 저장 장소의 주소값과 그 저장 장소에 들어 있는 값을 모두 나타낼 수 있는 변수
method
: a function (subroutine) associated with an object. A function defined in a class. Unless specified otherwise, a method is not static.
instance method
: Any method that is invoked with respect to an instance of a class.
class method
: A method that is invoked without reference to a particular object. Class methods affect the class as a whole, not a particular instance of the class. = static method
Message
Software objects interact and communicate with each other using messages.
Class
: a blueprint or prototype that defines the variables and the methods common to all objects of a certain kind.
Inheritance
A class inherits state and behavior from its superclass. Inheritance provides a powerful and natural mechanism for organizing and structuring software programs.
Interface
: a contract in the form of a collection of method and constant declarations. When a class implements an interface, it promises to implement all of the methods declared in that interface.
object-oriented design
: A software design method that models the characteristics of abstract or real objects using classes and objects.
Object
: a software bundle of related variables and methods. (Software objects are often used to model real-world objects you find in everyday life.)
A software object can represent real-world objects and abstract concepts like an event.
> what the software object knows is 'state' and what it can do is 'behavior'.

variable
: an item of data named by an identifier. Each variable has a type, such as int or Object, and a scope
컴퓨터 프로그래밍 언어에서의 변수의 의미는, 컴퓨터 기억 장소를 가리키는 추상적인 표현방법입니다. 즉, 기억 장소의 주소를 상징화한 것입니다. 변수에 대한 정의가 아직까지 정확하게 이해되지 않는 분들이 많으시리라 생각됩니다.
다른 예에 빗대자면 이렇습니다. '동경 135˚, 북위 37.5˚'가 메모리 주소라면, '한국(Korea)'은 이를 나타내는 변수(정확히 변수의 이름)가 되는 것입니다.
변수는 다음과 같은 속성을 가지고 있습니다.
이름(Name)
변수의 호칭입니다.
주소(Address)
변수와 연결되는 메모리의 위치를 말합니다. 이 때, 변수가 나타내는 메모리 위치는 항상 동일하지 않습니다. 즉, 동일한 이름을 가진 변수라도 이 변수가 각기 다른 용도로 쓰일 때에는 서로 독립적인 개체로 보고, 이들 변수가 가리키는 주소도 서로 다르게 됩니다. 변수의 주소를 가끔 'l-value'라고도 하는데, 이는 할당문에서 변수가 좌변에 위치한다는 사실에 기인한 것입니다.
값(Value)
변수의 값은 변수와 연결된 메모리 위치에 담겨 있는 내용을 말합니다. 'Apple'이라는 이름을 가진 변수의 메모리 주소가 '00DE'이고, 이 공간에 저장된 내용이 실수 '3.41'라고 하면, 이것이 바로 변수의 값이 되는 것입니다. 변수의 값을 가리켜 'r-value'라고도 합니다.
자료형(Type)
변수의 자료형은 변수가 가질 수 있는 값의 범위와 적용 가능한 연산자의 집합을 결정합니다. 예를 들어, C 언어에서 'int' 자료형은 -32768~32767 까지의 범위에 해당하는 값을 가질 수 있으며, 사칙연산 및 라이브러리 함수로 제공되는 연산자를 사용할 수 있습니다.
scope
:
class variable
: A data item associated with a particular class as a whole--not with particular instances of the class. Class variables are defined in class definitions. = static field
instance variable
: Any item of data that is associated with a particular object. Each instance of a class has its own copy of the instance variables defined in the class.
field
: A data member of a class. Unless specified otherwise, a field is not static.
- 수명에 따라
정적 변수(Static Variable)
스택 기반 동적 변수(Stack-Dynamic Variable)
명시적 힙 기반 동적 변수(Explicit Heap-Dynamic Variable)
묵시적 동적 변수(Implicit Dynamic Variable)
- 실효 범위(:변수의 값을 참조할 수 있는 범위, 즉 변수가 사용되는 문장의 범위)에 따라
local variable
: A data item known within a block, but inaccessible to code outside the block. For example, any variable defined within a method is a local variable and can't be used outside the method.
지역 변수는 변수가 선언된 프로그램 단일체나 함수 혹은 블록 안에서만 사용할 수 있는 변수
cf. 스택 기반 동적 변수(Static Dynamic Variable)는 선언문이 실행될 때 저장 장소 바인딩이 이루어지고, 그에 대한 자료형은 정적으로 바인딩 됩니다. 다시 말해서, 변수가 프로그램 시작 시에 바인딩 되는 것이 아니라, 프로그램을 한 줄 한 줄 수행하고 있는 동안, 변수를 선언하는 코드 부분이 나오면 그제서야 변수에 대한 저장 장소가 할당되고, 바인딩이 이루어지는 것입니다. 이러한 함수에서 선언되는 변수들을 지역 변수(Local Variable)라고 하는데, 지역 변수들에 대한 기억 장소가 바로 이 때 할당되며 함수의 수행이 모두 끝나면 반환됩니다.
non-local variable
: 비지역 변수는 전체 프로그램에 걸쳐 사용 가능한 변수를 말합니다.
pointer variable
: 포인터 변수는 저장 장소의 주소값과 그 저장 장소에 들어 있는 값을 모두 나타낼 수 있는 변수
method
: a function (subroutine) associated with an object. A function defined in a class. Unless specified otherwise, a method is not static.
instance method
: Any method that is invoked with respect to an instance of a class.
class method
: A method that is invoked without reference to a particular object. Class methods affect the class as a whole, not a particular instance of the class. = static method
Message
Software objects interact and communicate with each other using messages.
Class
: a blueprint or prototype that defines the variables and the methods common to all objects of a certain kind.
Inheritance
A class inherits state and behavior from its superclass. Inheritance provides a powerful and natural mechanism for organizing and structuring software programs.
Interface
: a contract in the form of a collection of method and constant declarations. When a class implements an interface, it promises to implement all of the methods declared in that interface.
'Computation > Language' 카테고리의 다른 글
| The Java™ Tutorials (0) | 2007.02.28 |
|---|---|
| The Java Technology (0) | 2007.02.28 |
| <HeadFirst Java> (0) | 2006.07.13 |
| Java (0) | 2006.05.17 |
| 프로그래밍 언어 개론 (0) | 2006.03.31 |
