2009. 8. 5. 14:36
Computer Vision
Oxford 대학 Active Vision Group에서 개발한
PTAM (Parallel Tracking and Mapping for Small AR Workspaces)
http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~gk/PTAM/
Questions? E-mail ptam@robots.ox.ac.uk
0. requirements 확인
readme 파일에서 언급하는 대로 프로세서와 그래픽카드를 확인하니
"Intel Core 2 Duo processors 2.4GHz+ are fine."이라고 했는데, 2.0이면 되지 않을까? 그래픽 카드는 동일한 것이니 문제 없고.
1. library dependency 확인
1-1. TooN 다운로드
TooN (Tom's object oriented Numerics)은 선형대수 (벡터, 매트릭스 연산)를 위해 Cambridge Machine Intelligence lab에서 개발한 C++ 라이브러리라고 한다.
ref. TooN Documentation (<- 공식 홈보다 정리가 잘 되어 있군.)
다음과 같은 명령으로 다운로드를 받는다.
실행 결과:
생성된 TooN 폴더에 들어가서
실행 결과:
1-1-1. 더 안정적인(?) 버전을 받으려면
실행 결과:
1-2. libCVD 다운로드
libCVD (Cambridge Video Dynamics)는 같은 연구실에서 만든 컴퓨터 비전 관련 이미지 처리를 위한 C++ 라이브러리
ref. CVD documentation
실행 결과:
1-3. Gvars3 다운로드
Gvars3 (configuration system library)
실행 결과:
2. 다운로드한 기반 라이브러리 설치
2-1. TooN 설치
2-1-1. configure file 실행
configure scripts는 source code를 compile하고 실행시킬 수 있게 만들어 주는 것.
생성된 TooN 폴더에 들어가서
실행 결과:
2-1-2. 설치
(TooN은 헤더파일들의 모음이므로 compile이 필요없다.)
실행 결과:
2-2. libCVD 설치
2-2-1. configure 파일 실행
생성된 libCVD 폴더에 들어가서
실행 결과:
2-2-2. documents 생성 (생략해도 되는 듯)
실행 결과:
doxygen이란 게 없어서 그런가 하고 찾아 봤더니
있길래, 설치하고
실행 결과:
[#M_더보기|접기|
다시 시도했더니
2-2-3. compile 컴파일하기
실행 결과:
2-2-4. install 설치하기
실행 결과:
2-3. Gvars3 설치
2-3-1. configure 파일 실행
Gvars3 폴더에 들어가서
실행 결과:
2-3-2. compile 컴파일하기
실행 결과:
2-3-3. install 설치하기
2-4. OS X에서의 컴파일링과 관련하여
ref. UNIX에서 컴파일하기
Porting UNIX/Linux Applications to Mac OS X: Compiling Your Code in Mac OS X
3. PTAM 컴파일
3-1. 해당 플랫폼의 빌드 파일을 PTAM source 디렉토리로 복사
내 (OS X의) 경우, PTAM/Build/OS X에 있는 모든 (두 개의) 파일 Makefile과 VideoSource_OSX.cc를 PTAM 폴더에 옮겼다.
3-2. video source 셋업
카메라에 맞는 video input file을 컴파일하도록 Makefile을 수정해 주어야 한다.
맥의 경우, (아마도 Logitech Quickcam Pro 5000 을 기준으로 하는) 하나의 소스 파일만이 존재하므로 그대로 두면 될 듯.
3-3. video source 추가
다른 비디오 소스들은 libCVD에 클래스로 만들어져 있다고 한다. 여기에 포함되어 있지 않은 경우에는 VideoSource_XYZ.cc 라는 식의 이름을 갖는 파일을 만들어서 넣어 주어야 한다.
3-4. compile
PTAM 폴더에 들어가서
실행 결과:
이 에러 메시지는 다음 링크에서 논의되고 있는 문제와 비슷한 상황인 것 같다.
http://en.allexperts.com/q/Unix-Linux-OS-1064/Compiling-OpenGL-unix-linux.htm
3-4-1. OpenGL on UNIX
PTAM이 OpenGL을 사용하고 있는데, OpenGL이 Mac에 기본으로 설치되어 있으므로 신경쓰지 않았던 부분이다. 물론 system의 public framework으로 들어가 있음을 확인할 수 있다. 그런데 UNIX 프로그램에서 접근할 수는 없는가? (인터넷에서 검색해 보아도 따로 설치할 수 있는 다운로드 링크나 방법을 찾을 수 없다.)
에러 메시지에 대한 정확한 진단 ->
문제의 Makefile을 들여다보고
(다음은 philphys 인용)
파란색 부분 - 각 소스코드를 컴파일한 다음 컴파일된 오브젝트 코드를 실행파일로 링크하는 부분. 여기서는 $(LINKFLAGS)에 링커 프로그램에 전달되는 옵션이 들어간다.
초록색 부분 - 컴파일할 오브젝트 코드의 리스트
분홍색 부분 - CC는 컴파일러 프로그램과 기본 옵션. COMPILEFLAGS는 컴파일러에 전달하는 옵션들, 여기에 헤더 파일의 위치를 정할 수 있다. LINKFLAGS는 컴파일된 오브젝트 코드를 실행파일로 링크하는 링커에 들어가는 옵션. 여기에 라이브러리의 위치와 사용할 라이브러리를 지정해 준다. 라이브러리의 위치는 -L 옵션으로, 구체적인 라이브러리 이름은 -l 옵션으로.
maetel: 사실 프레임웍 안에 gl.h 파일이 있는 위치는 다음과 같다.
/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Headers
philphys: "근데 코드에서는 그 헤더를 "GL/gl.h"로 찾는다는 게 문제. 이건 프레임웍 방식이 아닌 고전적인 유닉스 Xwindows의 OpenGL 방식이다. 즉 방금 보인 gl.h, glu.h 등이 있는 /usr/X11R6/include 를 COMPILERFLAGS에 -I 옵션으로 넣어 줘야 하는 게 아닐까."
Makefile을 다음과 같이 수정하고 (보라색 부분 추가)
그러고 보면 아래와 같은 설명이 있었던 것이다.
다시 컴파일 하니,
실행 결과:
설치 완료!
두 실행파일 PTAM과 CameraCalibrator이 생성되었다.
3-5. X11R6에 대하여
X11R6 = Xwindow Verion 11 Release 6
Xwindow
X.org
4. camera calibration
CameraCalibrator 파일을 실행시켜 카메라 캘리브레이션을 시도했더니 GUI 창이 뜨는데 연결된 웹캠(Logitech QuickCam Pro 4000)으로부터 입력을 받지 못 한다.
4-0. 증상
CameraCalibrator 실행파일을 열면, 다음과 같은 터미널 창이 새로 열린다.
그리고 Video란 이름의 GUI 창이 열리는데, 이때 아무런 설정을 바꾸지 않고 그대로 OK를 누르면 위의 터미널 창에 다음과 같은 메시지가 이어지면서 자동 종료된다.
그러므로 3-3의 문제 -- set up video source (비디오 소스 셋업) --로 돌아가야 한다.
즉, VideoSource_OSX.cc 파일을 수정해서 다시 컴파일한 후 실행해야 한다.
삽질...
알고 보니 ./는 현재 디렉토리를 말하나 보다. PTAM 폴더 밑에 바로 있다. 왜 못 봤을까...
열어 보니 다음과 같다.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Context-free_grammar
모두 주석 처리되어 있는 파일이다. 당장 해결해야 하는 에러는 아닌가 보다.
4-1. VideoSource_OSX.cc 파일 수정
오렌지 색 부분의 string이 출력되었으니, GetAndFillFrameBWandRGB 함수 아래 조건문에서 걸리지 않고 있음을 알 수 있다.
4-1-1. "Raw" 추가
그리고 콘솔에 다음 메시지가 나왔으므로
코드에서 else if(pvb->get_frame_format_string().find("uyvy") != string::npos) { } 아래 58줄에
다음과 같이 조건문을 하나 추가해 주었다.
이제 입력이 들어오기 시작한다! (thank kyu!)
그러나 위에서 보듯 size가 맞지 않고 frame이 겹치는 등 넘어갈 수 없는 문제가 있다. (오른쪽 이미지는 같은 상황에서의 비교를 위해 맥용 드라이버 macam에서의 입력을 캡쳐한 것.)
터미널에서의 결과:
4-1-2. YUV format 확인
Logitech QuickCam Pro 4000는 YUV420P라는 글을 어디선가 보고, 코드의 yuv422 부분을 yuv420p로 바꾸었으나 증상은 그대로이다.
ref. YUV422 또는 YUV411 또는 YUV420P
http://ozviz.wasp.uwa.edu.au/~pbourke/dataformats/yuv/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YUV
왼쪽: macam에서 캡쳐한 이미지 / 오른쪽: PTAM CameraCalibrator에서 보여지는 이미지
Logitech QuickCam Pro 4000
왼쪽: macam에서 캡쳐한 이미지 / 오른쪽: PTAM CameraCalibrator에서 보여지는 이미지
Logitech QuickCam® Communicate STX™
Xgl이란 것과 관련이 있나... 일주일에 걸쳐 무수한 삽질을 거듭하다가...
ref. http://developer.apple.com/quicktime/icefloe/dispatch020.html
코드의 yuv422 부분을 그대로 두고, 추가했던 "Raw" 경우의 조건문 안에서만 분홍색 부분처럼 바꾸니
된다! ㅜㅜ (thank jini!)
왼쪽: Logitech QuickCam® Communicate STX™ / 오른쪽: Logitech QuickCam Pro 4000
4-1-3. qtbuffer.h
cam_type<Rgb<byte> >
ref.
http://developer.apple.com/samplecode/ElectricImageComponent/listing2.html
수정한 VideoSource 파일
터미널 창:
4-2. Camera Calibrator 실행
5. PTAM 실행
iSight를 Netmate 1394B 9P Bilingual to 6P 케이블로 MacMini에 연결하여 해 보니 더 잘 된다.
rms error 0.3 이하로 깔끔하게 수렴된 카메라 파라미터의 계산값이 다음과 같은 식으로 나올 때,
Camera calib is [ 1.22033 1.62577 0.489375 0.641251 0.544352 ]
PTAM을 실행하면 위의 Logitech QuickCam 두 기종보다는 features를 보다 잘 잡는다. (아직은 많이 부족하지만...)
PTAM (Parallel Tracking and Mapping for Small AR Workspaces)
http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~gk/PTAM/
Questions? E-mail ptam@robots.ox.ac.uk
0. requirements 확인
readme 파일에서 언급하는 대로 프로세서와 그래픽카드를 확인하니
내가 설치할 컴퓨터 사양:
Model Name: Mac mini
Model Identifier: Macmini3,1
Processor Name: Intel Core 2 Duo
Processor Speed: 2 GHz
Number Of Processors: 1
Total Number Of Cores: 2
L2 Cache: 3 MB
Memory: 1 GB
Bus Speed: 1.07 GHz
Boot ROM Version: MM31.0081.B00
그래픽 카드:
NVIDIA GeForce 9400
Model Name: Mac mini
Model Identifier: Macmini3,1
Processor Name: Intel Core 2 Duo
Processor Speed: 2 GHz
Number Of Processors: 1
Total Number Of Cores: 2
L2 Cache: 3 MB
Memory: 1 GB
Bus Speed: 1.07 GHz
Boot ROM Version: MM31.0081.B00
그래픽 카드:
NVIDIA GeForce 9400
"Intel Core 2 Duo processors 2.4GHz+ are fine."이라고 했는데, 2.0이면 되지 않을까? 그래픽 카드는 동일한 것이니 문제 없고.
1. library dependency 확인
1. TooN - a header library for linear algebra셋 다 없으므로,
2. libCVD - a library for image handling, video capture and computer vision
3. Gvars3 - a run-time configuration/scripting library, this is a sub-project of libCVD.
1-1. TooN 다운로드
TooN (Tom's object oriented Numerics)은 선형대수 (벡터, 매트릭스 연산)를 위해 Cambridge Machine Intelligence lab에서 개발한 C++ 라이브러리라고 한다.
ref. TooN Documentation (<- 공식 홈보다 정리가 잘 되어 있군.)
다음과 같은 명령으로 다운로드를 받는다.
%% cvs -z3 -d:pserver:anonymous@cvs.savannah.nongnu.org:/sources/toon co TooN
실행 결과:
cvs checkout: warning: failed to open /Users/lym/.cvspass for reading: No such file or directory
cvs checkout: Updating TooN
U TooN/Authors
U TooN/COPYING
U TooN/Cholesky.h
U TooN/Doxyfile
U TooN/GPL.txt
U TooN/LU.h
U TooN/Lapack_Cholesky.h
U TooN/Makefile.in
U TooN/README
U TooN/SVD.h
U TooN/SymEigen.h
U TooN/TODO
U TooN/TooN.h
U TooN/configure
U TooN/configure.ac
U TooN/determinant.h
U TooN/gauss_jordan.h
U TooN/gaussian_elimination.h
U TooN/generated.h
U TooN/helpers.h
U TooN/irls.h
U TooN/lapack.h
U TooN/make_make_vector.awk
U TooN/make_typeof.awk
U TooN/se2.h
U TooN/se3.h
U TooN/sl.h
U TooN/so2.h
U TooN/so3.h
U TooN/wls.h
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/Documentation
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/benchmark
U TooN/benchmark/generate_solvers.m
U TooN/benchmark/solve_ax_equals_b.cc
U TooN/benchmark/solvers.cc
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/doc
U TooN/doc/COPYING_FDL
U TooN/doc/Makefile
U TooN/doc/documentation.h
U TooN/doc/linoperatorsdoc.h
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/internal
U TooN/internal/allocator.hh
U TooN/internal/builtin_typeof.h
U TooN/internal/comma.hh
U TooN/internal/config.hh
U TooN/internal/config.hh.in
U TooN/internal/dchecktest.hh
U TooN/internal/debug.hh
U TooN/internal/deprecated.hh
U TooN/internal/diagmatrix.h
U TooN/internal/make_vector.hh
U TooN/internal/matrix.hh
U TooN/internal/mbase.hh
U TooN/internal/objects.h
U TooN/internal/operators.hh
U TooN/internal/overfill_error.hh
U TooN/internal/reference.hh
U TooN/internal/size_mismatch.hh
U TooN/internal/slice_error.hh
U TooN/internal/typeof.hh
U TooN/internal/vbase.hh
U TooN/internal/vector.hh
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/optimization
U TooN/optimization/brent.h
U TooN/optimization/conjugate_gradient.h
U TooN/optimization/downhill_simplex.h
U TooN/optimization/golden_section.h
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/test
U TooN/test/SXX_test.cc
U TooN/test/as_foo.cc
U TooN/test/brent_test.cc
U TooN/test/cg_test.cc
U TooN/test/cg_view.gnuplot
U TooN/test/chol.cc
U TooN/test/diagslice.cc
U TooN/test/dynamic_test.cc
U TooN/test/gauss_jordan.cc
U TooN/test/gaussian_elimination_test.cc
U TooN/test/golden_test.cc
U TooN/test/identity_test.cc
U TooN/test/lutest.cc
U TooN/test/make_vector.cc
U TooN/test/makevector.cc
U TooN/test/mat_test.cc
U TooN/test/mat_test2.cc
U TooN/test/mmult_test.cc
U TooN/test/normalize_test.cc
U TooN/test/normalize_test2.cc
U TooN/test/scalars.cc
U TooN/test/simplex_test.cc
U TooN/test/simplex_view.gnuplot
U TooN/test/sl.cc
U TooN/test/svd_test.cc
U TooN/test/sym.cc
U TooN/test/test2.cc
U TooN/test/test3.cc
U TooN/test/test_foreign.cc
U TooN/test/un_project.cc
U TooN/test/vec_test.cc
cvs checkout: Updating TooN
U TooN/Authors
U TooN/COPYING
U TooN/Cholesky.h
U TooN/Doxyfile
U TooN/GPL.txt
U TooN/LU.h
U TooN/Lapack_Cholesky.h
U TooN/Makefile.in
U TooN/README
U TooN/SVD.h
U TooN/SymEigen.h
U TooN/TODO
U TooN/TooN.h
U TooN/configure
U TooN/configure.ac
U TooN/determinant.h
U TooN/gauss_jordan.h
U TooN/gaussian_elimination.h
U TooN/generated.h
U TooN/helpers.h
U TooN/irls.h
U TooN/lapack.h
U TooN/make_make_vector.awk
U TooN/make_typeof.awk
U TooN/se2.h
U TooN/se3.h
U TooN/sl.h
U TooN/so2.h
U TooN/so3.h
U TooN/wls.h
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/Documentation
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/benchmark
U TooN/benchmark/generate_solvers.m
U TooN/benchmark/solve_ax_equals_b.cc
U TooN/benchmark/solvers.cc
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/doc
U TooN/doc/COPYING_FDL
U TooN/doc/Makefile
U TooN/doc/documentation.h
U TooN/doc/linoperatorsdoc.h
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/internal
U TooN/internal/allocator.hh
U TooN/internal/builtin_typeof.h
U TooN/internal/comma.hh
U TooN/internal/config.hh
U TooN/internal/config.hh.in
U TooN/internal/dchecktest.hh
U TooN/internal/debug.hh
U TooN/internal/deprecated.hh
U TooN/internal/diagmatrix.h
U TooN/internal/make_vector.hh
U TooN/internal/matrix.hh
U TooN/internal/mbase.hh
U TooN/internal/objects.h
U TooN/internal/operators.hh
U TooN/internal/overfill_error.hh
U TooN/internal/reference.hh
U TooN/internal/size_mismatch.hh
U TooN/internal/slice_error.hh
U TooN/internal/typeof.hh
U TooN/internal/vbase.hh
U TooN/internal/vector.hh
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/optimization
U TooN/optimization/brent.h
U TooN/optimization/conjugate_gradient.h
U TooN/optimization/downhill_simplex.h
U TooN/optimization/golden_section.h
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/test
U TooN/test/SXX_test.cc
U TooN/test/as_foo.cc
U TooN/test/brent_test.cc
U TooN/test/cg_test.cc
U TooN/test/cg_view.gnuplot
U TooN/test/chol.cc
U TooN/test/diagslice.cc
U TooN/test/dynamic_test.cc
U TooN/test/gauss_jordan.cc
U TooN/test/gaussian_elimination_test.cc
U TooN/test/golden_test.cc
U TooN/test/identity_test.cc
U TooN/test/lutest.cc
U TooN/test/make_vector.cc
U TooN/test/makevector.cc
U TooN/test/mat_test.cc
U TooN/test/mat_test2.cc
U TooN/test/mmult_test.cc
U TooN/test/normalize_test.cc
U TooN/test/normalize_test2.cc
U TooN/test/scalars.cc
U TooN/test/simplex_test.cc
U TooN/test/simplex_view.gnuplot
U TooN/test/sl.cc
U TooN/test/svd_test.cc
U TooN/test/sym.cc
U TooN/test/test2.cc
U TooN/test/test3.cc
U TooN/test/test_foreign.cc
U TooN/test/un_project.cc
U TooN/test/vec_test.cc
생성된 TooN 폴더에 들어가서
%%% ./configure
실행 결과:
checking for g++... g++
checking for C++ compiler default output file name... a.out
checking whether the C++ compiler works... yes
checking whether we are cross compiling... no
checking for suffix of executables...
checking for suffix of object files... o
checking whether we are using the GNU C++ compiler... yes
checking whether g++ accepts -g... yes
checking for dgesvd_ in -llapack... yes
checking for decltype... no
checking for __typeof__... yes
checking for __attribute__((deprecated))... yes
You're on the development branch of TooN 2.0. Everything will probably work, but
the interface is a bit different from TooN-1.x
If you want TooN-1, then get it using:
cvs -z3 -d:pserver:anoncvs@cvs.savannah.nongnu.org:/cvsroot/toon co -r Maintenance_Branch_1_x TooN
or update what you currently have using:
cvs up -r Maintenance_Branch_1_x
or head over to:
http://mi.eng.cam.ac.uk/~er258/cvd/
Otherwise, please report any bugs you come across.
configure: creating ./config.status
config.status: creating Makefile
config.status: creating internal/config.hh
checking for C++ compiler default output file name... a.out
checking whether the C++ compiler works... yes
checking whether we are cross compiling... no
checking for suffix of executables...
checking for suffix of object files... o
checking whether we are using the GNU C++ compiler... yes
checking whether g++ accepts -g... yes
checking for dgesvd_ in -llapack... yes
checking for decltype... no
checking for __typeof__... yes
checking for __attribute__((deprecated))... yes
You're on the development branch of TooN 2.0. Everything will probably work, but
the interface is a bit different from TooN-1.x
If you want TooN-1, then get it using:
cvs -z3 -d:pserver:anoncvs@cvs.savannah.nongnu.org:/cvsroot/toon co -r Maintenance_Branch_1_x TooN
or update what you currently have using:
cvs up -r Maintenance_Branch_1_x
or head over to:
http://mi.eng.cam.ac.uk/~er258/cvd/
Otherwise, please report any bugs you come across.
configure: creating ./config.status
config.status: creating Makefile
config.status: creating internal/config.hh
1-1-1. 더 안정적인(?) 버전을 받으려면
%% cvs -z3 -d:pserver:anonymous@cvs.savannah.nongnu.org:/sources/toon co -D "Mon May 11 16:29:26 BST 2009" TooN
실행 결과:
cvs checkout: warning: failed to open /Users/lym/.cvspass for reading: No such file or directory
? TooN/Makefile
? TooN/config.log
? TooN/config.status
cvs checkout: Updating TooN
U TooN/Cholesky.h
U TooN/Doxyfile
U TooN/LU.h
U TooN/Makefile.in
U TooN/SVD.h
U TooN/SymEigen.h
U TooN/TooN.h
U TooN/configure
U TooN/configure.ac
cvs checkout: `TooN/determinant.h' is no longer in the repository
U TooN/gauss_jordan.h
U TooN/gaussian_elimination.h
U TooN/helpers.h
U TooN/irls.h
U TooN/se2.h
U TooN/se3.h
U TooN/sl.h
U TooN/so2.h
U TooN/so3.h
U TooN/util.h
U TooN/wls.h
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/Documentation
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/benchmark
U TooN/benchmark/generate_solvers.m
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/doc
U TooN/doc/documentation.h
U TooN/doc/matrixdoc.h
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/internal
U TooN/internal/allocator.hh
cvs checkout: `TooN/internal/comma.hh' is no longer in the repository
RCS file: /sources/toon/TooN/internal/config.hh,v
retrieving revision 1.12
retrieving revision 1.8
Merging differences between 1.12 and 1.8 into config.hh
TooN/internal/config.hh already contains the differences between 1.12 and 1.8
U TooN/internal/config.hh.in
cvs checkout: `TooN/internal/dchecktest.hh' is no longer in the repository
U TooN/internal/debug.hh
cvs checkout: `TooN/internal/deprecated.hh' is no longer in the repository
U TooN/internal/diagmatrix.h
U TooN/internal/matrix.hh
U TooN/internal/mbase.hh
U TooN/internal/objects.h
U TooN/internal/operators.hh
cvs checkout: `TooN/internal/overfill_error.hh' is no longer in the repository
U TooN/internal/reference.hh
U TooN/internal/slice_error.hh
U TooN/internal/vector.hh
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/optimization
U TooN/optimization/conjugate_gradient.h
U TooN/optimization/downhill_simplex.h
U TooN/optimization/golden_section.h
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/test
U TooN/test/identity_test.cc
cvs checkout: `TooN/test/simplex_test.cc' is no longer in the repository
cvs checkout: `TooN/test/simplex_view.gnuplot' is no longer in the repository
U TooN/test/vec_test.cc
? TooN/Makefile
? TooN/config.log
? TooN/config.status
cvs checkout: Updating TooN
U TooN/Cholesky.h
U TooN/Doxyfile
U TooN/LU.h
U TooN/Makefile.in
U TooN/SVD.h
U TooN/SymEigen.h
U TooN/TooN.h
U TooN/configure
U TooN/configure.ac
cvs checkout: `TooN/determinant.h' is no longer in the repository
U TooN/gauss_jordan.h
U TooN/gaussian_elimination.h
U TooN/helpers.h
U TooN/irls.h
U TooN/se2.h
U TooN/se3.h
U TooN/sl.h
U TooN/so2.h
U TooN/so3.h
U TooN/util.h
U TooN/wls.h
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/Documentation
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/benchmark
U TooN/benchmark/generate_solvers.m
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/doc
U TooN/doc/documentation.h
U TooN/doc/matrixdoc.h
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/internal
U TooN/internal/allocator.hh
cvs checkout: `TooN/internal/comma.hh' is no longer in the repository
RCS file: /sources/toon/TooN/internal/config.hh,v
retrieving revision 1.12
retrieving revision 1.8
Merging differences between 1.12 and 1.8 into config.hh
TooN/internal/config.hh already contains the differences between 1.12 and 1.8
U TooN/internal/config.hh.in
cvs checkout: `TooN/internal/dchecktest.hh' is no longer in the repository
U TooN/internal/debug.hh
cvs checkout: `TooN/internal/deprecated.hh' is no longer in the repository
U TooN/internal/diagmatrix.h
U TooN/internal/matrix.hh
U TooN/internal/mbase.hh
U TooN/internal/objects.h
U TooN/internal/operators.hh
cvs checkout: `TooN/internal/overfill_error.hh' is no longer in the repository
U TooN/internal/reference.hh
U TooN/internal/slice_error.hh
U TooN/internal/vector.hh
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/optimization
U TooN/optimization/conjugate_gradient.h
U TooN/optimization/downhill_simplex.h
U TooN/optimization/golden_section.h
cvs checkout: Updating TooN/test
U TooN/test/identity_test.cc
cvs checkout: `TooN/test/simplex_test.cc' is no longer in the repository
cvs checkout: `TooN/test/simplex_view.gnuplot' is no longer in the repository
U TooN/test/vec_test.cc
1-2. libCVD 다운로드
libCVD (Cambridge Video Dynamics)는 같은 연구실에서 만든 컴퓨터 비전 관련 이미지 처리를 위한 C++ 라이브러리
ref. CVD documentation
%% cvs -z3 -d:pserver:anonymous@cvs.savannah.nongnu.org:/sources/libcvd co -D "Mon May 11 16:29:26 BST 2009" libcvd
실행 결과:
cvs checkout: warning: failed to open /Users/lym/.cvspass for reading: No such file or directory
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd
U libcvd/Authors
U libcvd/Doxyfile
U libcvd/LICENSE
U libcvd/Makefile.in
U libcvd/TODO
U libcvd/config.guess
U libcvd/config.sub
U libcvd/configure
U libcvd/configure.in
U libcvd/generate_dependencies.bash
U libcvd/install-sh
U libcvd/subimage_test.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/build
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/build/vc2005
U libcvd/build/vc2005/config.h
U libcvd/build/vc2005/libcvd.sln
U libcvd/build/vc2005/libcvd.vcproj
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/build/vc2008
U libcvd/build/vc2008/libcvd.sln
U libcvd/build/vc2008/libcvd.vcproj
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd
U libcvd/cvd/abs.h
U libcvd/cvd/bresenham.h
U libcvd/cvd/brezenham.h
U libcvd/cvd/byte.h
U libcvd/cvd/camera.h
U libcvd/cvd/colourspace.h
U libcvd/cvd/colourspace_convert.h
U libcvd/cvd/colourspace_frame.h
U libcvd/cvd/colourspacebuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/colourspaces.h
U libcvd/cvd/connected_components.h
U libcvd/cvd/convolution.h
U libcvd/cvd/cpu_hacks.h
U libcvd/cvd/cvd_image.h
U libcvd/cvd/cvd_timer.h
U libcvd/cvd/deinterlacebuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/deinterlaceframe.h
U libcvd/cvd/diskbuffer2.h
U libcvd/cvd/diskbuffer2_frame.h
U libcvd/cvd/documentation.h
U libcvd/cvd/draw.h
U libcvd/cvd/eventobject.h
U libcvd/cvd/exceptions.h
U libcvd/cvd/fast_corner.h
U libcvd/cvd/gl_helpers.h
U libcvd/cvd/glwindow.h
U libcvd/cvd/haar.h
U libcvd/cvd/harris_corner.h
U libcvd/cvd/helpers.h
U libcvd/cvd/image.h
U libcvd/cvd/image_convert.h
U libcvd/cvd/image_convert_fwd.h
U libcvd/cvd/image_interpolate.h
U libcvd/cvd/image_io.h
U libcvd/cvd/image_ref.h
U libcvd/cvd/integral_image.h
U libcvd/cvd/interpolate.h
U libcvd/cvd/irls.h
U libcvd/cvd/la.h
U libcvd/cvd/localvideobuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/localvideoframe.h
U libcvd/cvd/message_queue.h
U libcvd/cvd/nonmax_suppression.h
U libcvd/cvd/random.h
U libcvd/cvd/readaheadvideobuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/rgb.h
U libcvd/cvd/rgb8.h
U libcvd/cvd/rgba.h
U libcvd/cvd/ringbuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/runnable.h
U libcvd/cvd/runnable_batch.h
U libcvd/cvd/se2.h
U libcvd/cvd/se3.h
U libcvd/cvd/serverpushjpegbuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/serverpushjpegframe.h
U libcvd/cvd/so2.h
U libcvd/cvd/so3.h
U libcvd/cvd/synchronized.h
U libcvd/cvd/tensor_voting.h
U libcvd/cvd/thread.h
U libcvd/cvd/timeddiskbuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/timer.h
U libcvd/cvd/utility.h
U libcvd/cvd/vector_image_ref.h
U libcvd/cvd/videobuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/videobufferflags.h
U libcvd/cvd/videodisplay.h
U libcvd/cvd/videofilebuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/videofilebuffer_frame.h
U libcvd/cvd/videoframe.h
U libcvd/cvd/videosource.h
U libcvd/cvd/vision.h
U libcvd/cvd/wls.h
U libcvd/cvd/wls_c.h
U libcvd/cvd/wls_cholesky.h
U libcvd/cvd/yc.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/IRIX
U libcvd/cvd/IRIX/O2buffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/IRIX/O2videoframe.h
U libcvd/cvd/IRIX/sgi-video.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/Linux
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/capture_logic.cxx
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/dvbuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/dvbuffer3.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/dvframe.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/v4l1buffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/v4l1frame.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/v4l2buffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/v4l2frame.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/v4lbuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/v4lcontrol.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/OSX
U libcvd/cvd/OSX/qtbuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/OSX/qtframe.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/internal
U libcvd/cvd/internal/aligned_mem.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/assembly.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/builtin_components.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/convert_pixel_types.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/disk_image.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/gl_types.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/image_ref_implementation.hh
U libcvd/cvd/internal/is_pod.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/load_and_save.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/name_CVD_rgb_types.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/name_builtin_types.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/pixel_operations.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/pixel_traits.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/rgb_components.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/scalar_convert.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/simple_vector.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/internal/io
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/bmp.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/fits.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/jpeg.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/png.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/pnm_grok.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/save_postscript.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/text.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/tiff.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/internal/pnm
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/lock
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/python
U libcvd/cvd/python/interface.h
U libcvd/cvd/python/selector.h
U libcvd/cvd/python/types.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src
U libcvd/cvd_src/bayer.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/brezenham.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/colourspace_convert.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/connected_components.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/convolution.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/corner_10.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/corner_12.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/corner_9.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/cvd_timer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/diskbuffer2.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/draw.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/draw_toon.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/eventobject.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/exceptions.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast_corner.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/faster_corner_10.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/faster_corner_12.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/faster_corner_9.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/faster_corner_utilities.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/globlist.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/gltext.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/glwindow.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/half_sample.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/image_io.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/mono.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/sans.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/serif.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/slower_corner_10.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/slower_corner_11.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/slower_corner_12.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/slower_corner_7.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/slower_corner_8.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/slower_corner_9.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/synchronized.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/tensor_voting.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/thread.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/utility_helpers.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/videodisplay.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/videofilebuffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/videosource.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/yuv411_to_stuff.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/yuv420.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/yuv422.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/yuv422.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/IRIX
U libcvd/cvd_src/IRIX/O2buffer.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/IRIX/sgi-video.cxx
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/Linux
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/dvbuffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/dvbuffer3_dc1394v1.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/dvbuffer3_dc1394v2.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/kernel-video1394.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/v4l1buffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/v4l2buffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/v4lbuffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/v4lcontrol.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/OSX
U libcvd/cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/SSE2
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/Win32
U libcvd/cvd_src/Win32/glwindow.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/Win32/win32.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/Win32/win32.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/fast
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/prototypes.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/i686
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/byte_to_double_gradient.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/byte_to_float_gradient.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/byte_to_short_difference.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/convert_rgb_to_y.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/convolve_float.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/convolve_float4.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/float_add_mul_add.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/float_add_mul_add_unaligned.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/float_assign_mul.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/float_difference.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/float_innerproduct.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/gradient.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/halfsample.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/int_difference.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/rgb_to_gray.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/short_difference.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/testconf
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/utility_float.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.C
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX_64.C
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/yuv420p_to_rgb.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/yuv422_to_grey.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/yuv422_to_rgb.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/yuv422_wrapper.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/noarch
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/convolve_gaussian.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/gradient.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/median_3x3.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/posix_memalign.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/utility_byte_differences.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/utility_double_int.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/utility_float.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/nothread
U libcvd/cvd_src/nothread/runnable_batch.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/posix
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/thread
U libcvd/cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/doc
U libcvd/doc/cameracalib2cm.pdf
U libcvd/doc/tutorial.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/make
U libcvd/make/compile_deps.awk
U libcvd/make/log_to_changelog.awk
U libcvd/make/march_flags
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/pnm_src
U libcvd/pnm_src/bmp.cxx
U libcvd/pnm_src/fits.cc
U libcvd/pnm_src/jpeg.cxx
U libcvd/pnm_src/png.cc
U libcvd/pnm_src/pnm_grok.cxx
U libcvd/pnm_src/save_postscript.cxx
U libcvd/pnm_src/text.cxx
U libcvd/pnm_src/text_write.cc
U libcvd/pnm_src/tiff.cxx
U libcvd/pnm_src/tiffwrite.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/progs
U libcvd/progs/calibrate.cxx
U libcvd/progs/cvd_display_image.cxx
U libcvd/progs/cvd_image_viewer.cxx
U libcvd/progs/img_play.cxx
U libcvd/progs/img_play_bw.cxx
U libcvd/progs/img_play_deinterlace.cxx
U libcvd/progs/img_play_generic.cxx
U libcvd/progs/se3_exp.cxx
U libcvd/progs/se3_inv.cxx
U libcvd/progs/se3_ln.cxx
U libcvd/progs/se3_post_mul.cxx
U libcvd/progs/se3_pre_mul.cxx
U libcvd/progs/video_play.cc
U libcvd/progs/video_play_bw.cc
U libcvd/progs/video_play_source.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/python
U libcvd/python/setup.py
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/python/CVD
U libcvd/python/CVD/cvd.cpp
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/test
U libcvd/test/diskbuffer2.cxx
U libcvd/test/dvbuffer3_bayerrgb.cxx
U libcvd/test/dvbuffer3_mono.cxx
U libcvd/test/dvbuffer_controls.cxx
U libcvd/test/dvbuffer_mono.cxx
U libcvd/test/dvbuffer_rgb.cxx
U libcvd/test/dvbuffer_yuvrgb.cxx
U libcvd/test/fast_test.cxx
U libcvd/test/floodfill_test.cc
U libcvd/test/font.cpp
U libcvd/test/o2buffer.cxx
U libcvd/test/test_images.cxx
U libcvd/test/v4l1buffer_bayer.cxx
U libcvd/test/v4l1buffer_mono.cxx
U libcvd/test/v4l1buffer_rgb.cxx
U libcvd/test/v4l2buffer.cxx
U libcvd/test/v4lbuffer_bayerrgb.cxx
U libcvd/test/v4lbuffer_mono.cxx
U libcvd/test/videoprog.cxx
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/test/fast_test_image
U libcvd/test/fast_test_image/noise.pgm
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/test/images
U libcvd/test/images/1-byte-bin.pgm
U libcvd/test/images/1-byte-bin.ppm
U libcvd/test/images/1-byte-txt.pgm
U libcvd/test/images/1-byte-txt.ppm
U libcvd/test/images/2-byte-bin.pgm
U libcvd/test/images/2-byte-bin.ppm
U libcvd/test/images/2-byte-txt.pgm
U libcvd/test/images/2-byte-txt.ppm
U libcvd/test/images/colour.jpg
U libcvd/test/images/grey.jpg
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/test/images/tiff
U libcvd/test/images/tiff/grey-bool-inverted.tiff
U libcvd/test/images/tiff/grey-uint16-normal.tiff
U libcvd/test/images/tiff/grey-uint8-normal.tiff
U libcvd/test/images/tiff/rgb-uint16.tiff
U libcvd/test/images/tiff/rgb-uint8.tiff
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/util
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd
U libcvd/Authors
U libcvd/Doxyfile
U libcvd/LICENSE
U libcvd/Makefile.in
U libcvd/TODO
U libcvd/config.guess
U libcvd/config.sub
U libcvd/configure
U libcvd/configure.in
U libcvd/generate_dependencies.bash
U libcvd/install-sh
U libcvd/subimage_test.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/build
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/build/vc2005
U libcvd/build/vc2005/config.h
U libcvd/build/vc2005/libcvd.sln
U libcvd/build/vc2005/libcvd.vcproj
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/build/vc2008
U libcvd/build/vc2008/libcvd.sln
U libcvd/build/vc2008/libcvd.vcproj
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd
U libcvd/cvd/abs.h
U libcvd/cvd/bresenham.h
U libcvd/cvd/brezenham.h
U libcvd/cvd/byte.h
U libcvd/cvd/camera.h
U libcvd/cvd/colourspace.h
U libcvd/cvd/colourspace_convert.h
U libcvd/cvd/colourspace_frame.h
U libcvd/cvd/colourspacebuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/colourspaces.h
U libcvd/cvd/connected_components.h
U libcvd/cvd/convolution.h
U libcvd/cvd/cpu_hacks.h
U libcvd/cvd/cvd_image.h
U libcvd/cvd/cvd_timer.h
U libcvd/cvd/deinterlacebuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/deinterlaceframe.h
U libcvd/cvd/diskbuffer2.h
U libcvd/cvd/diskbuffer2_frame.h
U libcvd/cvd/documentation.h
U libcvd/cvd/draw.h
U libcvd/cvd/eventobject.h
U libcvd/cvd/exceptions.h
U libcvd/cvd/fast_corner.h
U libcvd/cvd/gl_helpers.h
U libcvd/cvd/glwindow.h
U libcvd/cvd/haar.h
U libcvd/cvd/harris_corner.h
U libcvd/cvd/helpers.h
U libcvd/cvd/image.h
U libcvd/cvd/image_convert.h
U libcvd/cvd/image_convert_fwd.h
U libcvd/cvd/image_interpolate.h
U libcvd/cvd/image_io.h
U libcvd/cvd/image_ref.h
U libcvd/cvd/integral_image.h
U libcvd/cvd/interpolate.h
U libcvd/cvd/irls.h
U libcvd/cvd/la.h
U libcvd/cvd/localvideobuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/localvideoframe.h
U libcvd/cvd/message_queue.h
U libcvd/cvd/nonmax_suppression.h
U libcvd/cvd/random.h
U libcvd/cvd/readaheadvideobuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/rgb.h
U libcvd/cvd/rgb8.h
U libcvd/cvd/rgba.h
U libcvd/cvd/ringbuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/runnable.h
U libcvd/cvd/runnable_batch.h
U libcvd/cvd/se2.h
U libcvd/cvd/se3.h
U libcvd/cvd/serverpushjpegbuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/serverpushjpegframe.h
U libcvd/cvd/so2.h
U libcvd/cvd/so3.h
U libcvd/cvd/synchronized.h
U libcvd/cvd/tensor_voting.h
U libcvd/cvd/thread.h
U libcvd/cvd/timeddiskbuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/timer.h
U libcvd/cvd/utility.h
U libcvd/cvd/vector_image_ref.h
U libcvd/cvd/videobuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/videobufferflags.h
U libcvd/cvd/videodisplay.h
U libcvd/cvd/videofilebuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/videofilebuffer_frame.h
U libcvd/cvd/videoframe.h
U libcvd/cvd/videosource.h
U libcvd/cvd/vision.h
U libcvd/cvd/wls.h
U libcvd/cvd/wls_c.h
U libcvd/cvd/wls_cholesky.h
U libcvd/cvd/yc.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/IRIX
U libcvd/cvd/IRIX/O2buffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/IRIX/O2videoframe.h
U libcvd/cvd/IRIX/sgi-video.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/Linux
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/capture_logic.cxx
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/dvbuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/dvbuffer3.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/dvframe.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/v4l1buffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/v4l1frame.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/v4l2buffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/v4l2frame.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/v4lbuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/Linux/v4lcontrol.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/OSX
U libcvd/cvd/OSX/qtbuffer.h
U libcvd/cvd/OSX/qtframe.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/internal
U libcvd/cvd/internal/aligned_mem.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/assembly.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/builtin_components.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/convert_pixel_types.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/disk_image.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/gl_types.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/image_ref_implementation.hh
U libcvd/cvd/internal/is_pod.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/load_and_save.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/name_CVD_rgb_types.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/name_builtin_types.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/pixel_operations.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/pixel_traits.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/rgb_components.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/scalar_convert.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/simple_vector.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/internal/io
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/bmp.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/fits.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/jpeg.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/png.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/pnm_grok.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/save_postscript.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/text.h
U libcvd/cvd/internal/io/tiff.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/internal/pnm
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/lock
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd/python
U libcvd/cvd/python/interface.h
U libcvd/cvd/python/selector.h
U libcvd/cvd/python/types.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src
U libcvd/cvd_src/bayer.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/brezenham.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/colourspace_convert.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/connected_components.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/convolution.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/corner_10.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/corner_12.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/corner_9.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/cvd_timer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/diskbuffer2.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/draw.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/draw_toon.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/eventobject.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/exceptions.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast_corner.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/faster_corner_10.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/faster_corner_12.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/faster_corner_9.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/faster_corner_utilities.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/globlist.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/gltext.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/glwindow.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/half_sample.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/image_io.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/mono.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/sans.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/serif.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/slower_corner_10.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/slower_corner_11.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/slower_corner_12.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/slower_corner_7.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/slower_corner_8.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/slower_corner_9.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/synchronized.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/tensor_voting.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/thread.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/utility_helpers.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/videodisplay.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/videofilebuffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/videosource.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/yuv411_to_stuff.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/yuv420.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/yuv422.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/yuv422.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/IRIX
U libcvd/cvd_src/IRIX/O2buffer.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/IRIX/sgi-video.cxx
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/Linux
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/dvbuffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/dvbuffer3_dc1394v1.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/dvbuffer3_dc1394v2.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/kernel-video1394.h
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/v4l1buffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/v4l2buffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/v4lbuffer.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/Linux/v4lcontrol.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/OSX
U libcvd/cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/SSE2
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/Win32
U libcvd/cvd_src/Win32/glwindow.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/Win32/win32.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/Win32/win32.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/fast
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.cxx
U libcvd/cvd_src/fast/prototypes.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/i686
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/byte_to_double_gradient.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/byte_to_float_gradient.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/byte_to_short_difference.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/convert_rgb_to_y.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/convolve_float.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/convolve_float4.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/float_add_mul_add.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/float_add_mul_add_unaligned.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/float_assign_mul.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/float_difference.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/float_innerproduct.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/gradient.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/halfsample.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/int_difference.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/rgb_to_gray.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/short_difference.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/testconf
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/utility_float.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.C
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX_64.C
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/yuv420p_to_rgb.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/yuv422_to_grey.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/yuv422_to_rgb.s
U libcvd/cvd_src/i686/yuv422_wrapper.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/noarch
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/convolve_gaussian.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/gradient.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/median_3x3.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/posix_memalign.cpp
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/utility_byte_differences.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/utility_double_int.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/utility_float.cc
U libcvd/cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/nothread
U libcvd/cvd_src/nothread/runnable_batch.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/posix
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/cvd_src/thread
U libcvd/cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/doc
U libcvd/doc/cameracalib2cm.pdf
U libcvd/doc/tutorial.h
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/make
U libcvd/make/compile_deps.awk
U libcvd/make/log_to_changelog.awk
U libcvd/make/march_flags
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/pnm_src
U libcvd/pnm_src/bmp.cxx
U libcvd/pnm_src/fits.cc
U libcvd/pnm_src/jpeg.cxx
U libcvd/pnm_src/png.cc
U libcvd/pnm_src/pnm_grok.cxx
U libcvd/pnm_src/save_postscript.cxx
U libcvd/pnm_src/text.cxx
U libcvd/pnm_src/text_write.cc
U libcvd/pnm_src/tiff.cxx
U libcvd/pnm_src/tiffwrite.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/progs
U libcvd/progs/calibrate.cxx
U libcvd/progs/cvd_display_image.cxx
U libcvd/progs/cvd_image_viewer.cxx
U libcvd/progs/img_play.cxx
U libcvd/progs/img_play_bw.cxx
U libcvd/progs/img_play_deinterlace.cxx
U libcvd/progs/img_play_generic.cxx
U libcvd/progs/se3_exp.cxx
U libcvd/progs/se3_inv.cxx
U libcvd/progs/se3_ln.cxx
U libcvd/progs/se3_post_mul.cxx
U libcvd/progs/se3_pre_mul.cxx
U libcvd/progs/video_play.cc
U libcvd/progs/video_play_bw.cc
U libcvd/progs/video_play_source.cc
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/python
U libcvd/python/setup.py
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/python/CVD
U libcvd/python/CVD/cvd.cpp
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/test
U libcvd/test/diskbuffer2.cxx
U libcvd/test/dvbuffer3_bayerrgb.cxx
U libcvd/test/dvbuffer3_mono.cxx
U libcvd/test/dvbuffer_controls.cxx
U libcvd/test/dvbuffer_mono.cxx
U libcvd/test/dvbuffer_rgb.cxx
U libcvd/test/dvbuffer_yuvrgb.cxx
U libcvd/test/fast_test.cxx
U libcvd/test/floodfill_test.cc
U libcvd/test/font.cpp
U libcvd/test/o2buffer.cxx
U libcvd/test/test_images.cxx
U libcvd/test/v4l1buffer_bayer.cxx
U libcvd/test/v4l1buffer_mono.cxx
U libcvd/test/v4l1buffer_rgb.cxx
U libcvd/test/v4l2buffer.cxx
U libcvd/test/v4lbuffer_bayerrgb.cxx
U libcvd/test/v4lbuffer_mono.cxx
U libcvd/test/videoprog.cxx
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/test/fast_test_image
U libcvd/test/fast_test_image/noise.pgm
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/test/images
U libcvd/test/images/1-byte-bin.pgm
U libcvd/test/images/1-byte-bin.ppm
U libcvd/test/images/1-byte-txt.pgm
U libcvd/test/images/1-byte-txt.ppm
U libcvd/test/images/2-byte-bin.pgm
U libcvd/test/images/2-byte-bin.ppm
U libcvd/test/images/2-byte-txt.pgm
U libcvd/test/images/2-byte-txt.ppm
U libcvd/test/images/colour.jpg
U libcvd/test/images/grey.jpg
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/test/images/tiff
U libcvd/test/images/tiff/grey-bool-inverted.tiff
U libcvd/test/images/tiff/grey-uint16-normal.tiff
U libcvd/test/images/tiff/grey-uint8-normal.tiff
U libcvd/test/images/tiff/rgb-uint16.tiff
U libcvd/test/images/tiff/rgb-uint8.tiff
cvs checkout: Updating libcvd/util
1-3. Gvars3 다운로드
Gvars3 (configuration system library)
%% cvs -z3 -d:pserver:anonymous@cvs.savannah.nongnu.org:/sources/libcvd co -D "Mon May 11 16:29:26 BST 2009" gvars3
실행 결과:
cvs checkout: warning: failed to open /Users/lym/.cvspass for reading: No such file or directory
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3
U gvars3/Authors
U gvars3/GVars2.h.historic
U gvars3/LICENSE
U gvars3/Makefile.in
U gvars3/config.guess
U gvars3/config.sub
U gvars3/configure
U gvars3/configure.ac
U gvars3/fltk2_test
U gvars3/fltk_test
U gvars3/install-sh
U gvars3/main.cc
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3/build
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3/build/vc2005
U gvars3/build/vc2005/gvars3-headless.vcproj
U gvars3/build/vc2005/gvars3.sln
U gvars3/build/vc2005/gvars3.vcproj
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3/build/vc2008
U gvars3/build/vc2008/gvars3-headless.vcproj
U gvars3/build/vc2008/gvars3.sln
U gvars3/build/vc2008/gvars3.vcproj
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3/gvars2_compat
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3/gvars3
U gvars3/gvars3/GStringUtil.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI_Fltk.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI_Fltk2.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI_Motif.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI_Widgets.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI_non_readline.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI_readline.h
U gvars3/gvars3/config.h.in
U gvars3/gvars3/default.h
U gvars3/gvars3/gv3_implementation.hh
U gvars3/gvars3/gvars3.h
U gvars3/gvars3/instances.h
U gvars3/gvars3/serialize.h
U gvars3/gvars3/type_name.h
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3/src
U gvars3/src/GStringUtil.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_Fltk.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_Fltk2.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_Motif.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_impl.h
U gvars3/src/GUI_impl_headless.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_impl_noreadline.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_impl_readline.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_language.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_non_readline.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_none.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_readline.cc
U gvars3/src/gvars2.cc
U gvars3/src/gvars3.cc
U gvars3/src/inst.cc
U gvars3/src/inst_headless.cc
U gvars3/src/serialize.cc
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3
U gvars3/Authors
U gvars3/GVars2.h.historic
U gvars3/LICENSE
U gvars3/Makefile.in
U gvars3/config.guess
U gvars3/config.sub
U gvars3/configure
U gvars3/configure.ac
U gvars3/fltk2_test
U gvars3/fltk_test
U gvars3/install-sh
U gvars3/main.cc
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3/build
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3/build/vc2005
U gvars3/build/vc2005/gvars3-headless.vcproj
U gvars3/build/vc2005/gvars3.sln
U gvars3/build/vc2005/gvars3.vcproj
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3/build/vc2008
U gvars3/build/vc2008/gvars3-headless.vcproj
U gvars3/build/vc2008/gvars3.sln
U gvars3/build/vc2008/gvars3.vcproj
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3/gvars2_compat
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3/gvars3
U gvars3/gvars3/GStringUtil.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI_Fltk.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI_Fltk2.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI_Motif.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI_Widgets.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI_non_readline.h
U gvars3/gvars3/GUI_readline.h
U gvars3/gvars3/config.h.in
U gvars3/gvars3/default.h
U gvars3/gvars3/gv3_implementation.hh
U gvars3/gvars3/gvars3.h
U gvars3/gvars3/instances.h
U gvars3/gvars3/serialize.h
U gvars3/gvars3/type_name.h
cvs checkout: Updating gvars3/src
U gvars3/src/GStringUtil.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_Fltk.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_Fltk2.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_Motif.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_impl.h
U gvars3/src/GUI_impl_headless.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_impl_noreadline.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_impl_readline.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_language.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_non_readline.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_none.cc
U gvars3/src/GUI_readline.cc
U gvars3/src/gvars2.cc
U gvars3/src/gvars3.cc
U gvars3/src/inst.cc
U gvars3/src/inst_headless.cc
U gvars3/src/serialize.cc
2. 다운로드한 기반 라이브러리 설치
2-1. TooN 설치
2-1-1. configure file 실행
configure scripts는 source code를 compile하고 실행시킬 수 있게 만들어 주는 것.
생성된 TooN 폴더에 들어가서
%%% ./configure
실행 결과:
checking for g++... g++
checking for C++ compiler default output file name... a.out
checking whether the C++ compiler works... yes
checking whether we are cross compiling... no
checking for suffix of executables...
checking for suffix of object files... o
checking whether we are using the GNU C++ compiler... yes
checking whether g++ accepts -g... yes
checking for decltype... no
checking for typeof... yes
You're on the development branch of TooN 2.0. Everything will probably work, but
the interface is a bit different from TooN-1.x
If you want TooN-1, then get it using:
cvs -z3 -d:pserver:anoncvs@cvs.savannah.nongnu.org:/cvsroot/toon co -r Maintenance_Branch_1_x TooN
or update what you currently have using:
cvs up -r Maintenance_Branch_1_x
or head over to:
http://mi.eng.cam.ac.uk/~er258/cvd/
Otherwise, please report any bugs you come across.
configure: creating ./config.status
config.status: creating Makefile
config.status: creating internal/config.hh
checking for C++ compiler default output file name... a.out
checking whether the C++ compiler works... yes
checking whether we are cross compiling... no
checking for suffix of executables...
checking for suffix of object files... o
checking whether we are using the GNU C++ compiler... yes
checking whether g++ accepts -g... yes
checking for decltype... no
checking for typeof... yes
You're on the development branch of TooN 2.0. Everything will probably work, but
the interface is a bit different from TooN-1.x
If you want TooN-1, then get it using:
cvs -z3 -d:pserver:anoncvs@cvs.savannah.nongnu.org:/cvsroot/toon co -r Maintenance_Branch_1_x TooN
or update what you currently have using:
cvs up -r Maintenance_Branch_1_x
or head over to:
http://mi.eng.cam.ac.uk/~er258/cvd/
Otherwise, please report any bugs you come across.
configure: creating ./config.status
config.status: creating Makefile
config.status: creating internal/config.hh
2-1-2. 설치
(TooN은 헤더파일들의 모음이므로 compile이 필요없다.)
%%% sudo make install
실행 결과:
mkdir -p //usr/local/include/TooN
cp *.h //usr/local/include/TooN
cp -r optimization //usr/local/include/TooN/
cp -r internal //usr/local/include/TooN/
cp *.h //usr/local/include/TooN
cp -r optimization //usr/local/include/TooN/
cp -r internal //usr/local/include/TooN/
2-2. libCVD 설치
2-2-1. configure 파일 실행
생성된 libCVD 폴더에 들어가서
%%% export CXXFLAGS=-D_REENTRANT
%%% ./configure --without-ffmpeg
%%% ./configure --without-ffmpeg
실행 결과:
checking for gcc... gcc
checking for C compiler default output file name... a.out
checking whether the C compiler works... yes
checking whether we are cross compiling... no
checking for suffix of executables...
checking for suffix of object files... o
checking whether we are using the GNU C compiler... yes
checking whether gcc accepts -g... yes
checking for gcc option to accept ISO C89... none needed
checking how to run the C preprocessor... gcc -E
checking for grep that handles long lines and -e... /usr/bin/grep
checking for egrep... /usr/bin/grep -E
checking for ANSI C header files... yes
checking for gawk... no
checking for mawk... no
checking for nawk... no
checking for awk... awk
checking for g++... g++
checking whether we are using the GNU C++ compiler... yes
checking whether g++ accepts -g... yes
checking for a BSD-compatible install... /usr/bin/install -c
checking whether ln -s works... yes
checking for ranlib... ranlib
checking how to run the C++ preprocessor... g++ -E
checking if compiler flag -Wall works... yes
checking if compiler flag -Wextra works... yes
checking if compiler flag -pipe works... yes
checking if compiler flag -ggdb works... yes
checking if compiler flag -fPIC works... yes
checking build system type... i386-apple-darwin9.7.0
checking host system type... i386-apple-darwin9.7.0
checking for best optimize flags...
checking if compiler flag -O3 works... yes
checking CPU type... unknown
------------------------------------
Checking processor specific features
------------------------------------
checking for sys/types.h... yes
checking for sys/stat.h... yes
checking for stdlib.h... yes
checking for string.h... yes
checking for memory.h... yes
checking for strings.h... yes
checking for inttypes.h... yes
checking for stdint.h... yes
checking for unistd.h... yes
checking whether byte ordering is bigendian... no
checking for MMX support... yes
checking for MMXEXT support... yes
checking for SSE support... yes
checking for SSE2 support... yes
checking for SSE3 support... yes
checking for void*... yes
checking size of void*... 4
checking for inline asm statement... yes
checking assembler supports .type pseudo-op... no
-----------------------------------------------
Checking for operating system specific features
-----------------------------------------------
checking dc1394/dc1394.h usability... no
checking dc1394/dc1394.h presence... no
checking for dc1394/dc1394.h... no
checking for main in -ldc1394... no
checking for /opt/local... yes
checking for /sw... no
configure: Adding /usr/X11R6/include to the build path.
checking Carbon and QuickTime framework... yes
-------------------------------
Checking for optional libraries
-------------------------------
checking for X... libraries /usr/X11/lib, headers /usr/X11/include
checking for glDrawPixels in -lGL... yes
checking GL/glu.h usability... yes
checking GL/glu.h presence... yes
checking for GL/glu.h... yes
checking for gluGetString in -lGLU... yes
checking for tr1::shared_ptr... yes
checking for TooN... yes
checking Old TooN... no
checking for dgesvd_ in -lacml... no
checking if Accelerate framework is needed for LAPACK...
checking for dgesvd_... yes
checking for working pthreads... yes
checking for pthread_yield... no
checking for pthread_yield_np... yes
checking png.h usability... yes
checking png.h presence... yes
checking for png.h... yes
checking for png_init_io in -lpng... yes
checking jpeglib.h usability... yes
checking jpeglib.h presence... yes
checking for jpeglib.h... yes
checking for jpeg_destroy_decompress in -ljpeg... yes
checking JPEG read buffer size... 1 (safe reading)
checking tiffio.h usability... yes
checking tiffio.h presence... yes
checking for tiffio.h... yes
checking for TIFFReadRGBAImage in -ltiff... yes
checking for TIFFReadRGBAImageOriented in -ltiff... yes
checking for doxygen... no
-----------------------------------
Checking for platform compatibility
-----------------------------------
checking glob.h usability... yes
checking glob.h presence... yes
checking for glob.h... yes
checking for glob... yes
checking for GLOB_BRACE and GLOB_TILDE in glob.h... yes
checking whether feenableexcept is declared... no
checking for posix_memalign... no
--------------------------------
Checking for extra build options
--------------------------------
Options:
inline_asm qtbuffer videodisplay tr1_shared_ptr toon lapack pthread png jpeg tiff glob
Missing options for darwin9.7.0:
assembler dc1394v2 dvbuffer3 ffmpeg memalign
Dodgy things:
missing_c99_feenableexcept no_posix_memalign
SIMD support:
mmx mmxext sse sse2 sse3
Missing SIMD support for i386-apple-darwin9.7.0:
-D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread
-ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
-n Generating config...
diff: cvd/config.h: No such file or directory
New configuration
configure: creating ./config.status
config.status: creating Makefile
config.status: WARNING: Makefile.in seems to ignore the --datarootdir setting
checking for C compiler default output file name... a.out
checking whether the C compiler works... yes
checking whether we are cross compiling... no
checking for suffix of executables...
checking for suffix of object files... o
checking whether we are using the GNU C compiler... yes
checking whether gcc accepts -g... yes
checking for gcc option to accept ISO C89... none needed
checking how to run the C preprocessor... gcc -E
checking for grep that handles long lines and -e... /usr/bin/grep
checking for egrep... /usr/bin/grep -E
checking for ANSI C header files... yes
checking for gawk... no
checking for mawk... no
checking for nawk... no
checking for awk... awk
checking for g++... g++
checking whether we are using the GNU C++ compiler... yes
checking whether g++ accepts -g... yes
checking for a BSD-compatible install... /usr/bin/install -c
checking whether ln -s works... yes
checking for ranlib... ranlib
checking how to run the C++ preprocessor... g++ -E
checking if compiler flag -Wall works... yes
checking if compiler flag -Wextra works... yes
checking if compiler flag -pipe works... yes
checking if compiler flag -ggdb works... yes
checking if compiler flag -fPIC works... yes
checking build system type... i386-apple-darwin9.7.0
checking host system type... i386-apple-darwin9.7.0
checking for best optimize flags...
checking if compiler flag -O3 works... yes
checking CPU type... unknown
------------------------------------
Checking processor specific features
------------------------------------
checking for sys/types.h... yes
checking for sys/stat.h... yes
checking for stdlib.h... yes
checking for string.h... yes
checking for memory.h... yes
checking for strings.h... yes
checking for inttypes.h... yes
checking for stdint.h... yes
checking for unistd.h... yes
checking whether byte ordering is bigendian... no
checking for MMX support... yes
checking for MMXEXT support... yes
checking for SSE support... yes
checking for SSE2 support... yes
checking for SSE3 support... yes
checking for void*... yes
checking size of void*... 4
checking for inline asm statement... yes
checking assembler supports .type pseudo-op... no
-----------------------------------------------
Checking for operating system specific features
-----------------------------------------------
checking dc1394/dc1394.h usability... no
checking dc1394/dc1394.h presence... no
checking for dc1394/dc1394.h... no
checking for main in -ldc1394... no
checking for /opt/local... yes
checking for /sw... no
configure: Adding /usr/X11R6/include to the build path.
checking Carbon and QuickTime framework... yes
-------------------------------
Checking for optional libraries
-------------------------------
checking for X... libraries /usr/X11/lib, headers /usr/X11/include
checking for glDrawPixels in -lGL... yes
checking GL/glu.h usability... yes
checking GL/glu.h presence... yes
checking for GL/glu.h... yes
checking for gluGetString in -lGLU... yes
checking for tr1::shared_ptr... yes
checking for TooN... yes
checking Old TooN... no
checking for dgesvd_ in -lacml... no
checking if Accelerate framework is needed for LAPACK...
checking for dgesvd_... yes
checking for working pthreads... yes
checking for pthread_yield... no
checking for pthread_yield_np... yes
checking png.h usability... yes
checking png.h presence... yes
checking for png.h... yes
checking for png_init_io in -lpng... yes
checking jpeglib.h usability... yes
checking jpeglib.h presence... yes
checking for jpeglib.h... yes
checking for jpeg_destroy_decompress in -ljpeg... yes
checking JPEG read buffer size... 1 (safe reading)
checking tiffio.h usability... yes
checking tiffio.h presence... yes
checking for tiffio.h... yes
checking for TIFFReadRGBAImage in -ltiff... yes
checking for TIFFReadRGBAImageOriented in -ltiff... yes
checking for doxygen... no
-----------------------------------
Checking for platform compatibility
-----------------------------------
checking glob.h usability... yes
checking glob.h presence... yes
checking for glob.h... yes
checking for glob... yes
checking for GLOB_BRACE and GLOB_TILDE in glob.h... yes
checking whether feenableexcept is declared... no
checking for posix_memalign... no
--------------------------------
Checking for extra build options
--------------------------------
Options:
inline_asm qtbuffer videodisplay tr1_shared_ptr toon lapack pthread png jpeg tiff glob
Missing options for darwin9.7.0:
assembler dc1394v2 dvbuffer3 ffmpeg memalign
Dodgy things:
missing_c99_feenableexcept no_posix_memalign
SIMD support:
mmx mmxext sse sse2 sse3
Missing SIMD support for i386-apple-darwin9.7.0:
-D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread
-ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
-n Generating config...
diff: cvd/config.h: No such file or directory
New configuration
configure: creating ./config.status
config.status: creating Makefile
config.status: WARNING: Makefile.in seems to ignore the --datarootdir setting
2-2-2. documents 생성 (생략해도 되는 듯)
%% make docs
실행 결과:
Makefile:304: .deps: No such file or directory
rm -f .sourcefiles
find . -name "*.cxx" -o -name "*.cc" -o -name "*.cpp" -o -name "*.c" -o -name "*.C" > .sourcefiles
rm -f .deps
bash generate_dependencies.bash "-I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread" > .deps
./cvd_src/Linux/dvbuffer.cc:114:3: error: #error I dont know how to compile DC stuff for this kernel version!
./cvd_src/Linux/v4l2buffer.cc:79:3: error: #error "Can't do v4l2 for this kernel version"
make: *** No rule to make target `docs'. Stop.
rm -f .sourcefiles
find . -name "*.cxx" -o -name "*.cc" -o -name "*.cpp" -o -name "*.c" -o -name "*.C" > .sourcefiles
rm -f .deps
bash generate_dependencies.bash "-I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread" > .deps
./cvd_src/Linux/dvbuffer.cc:114:3: error: #error I dont know how to compile DC stuff for this kernel version!
./cvd_src/Linux/v4l2buffer.cc:79:3: error: #error "Can't do v4l2 for this kernel version"
make: *** No rule to make target `docs'. Stop.
doxygen이란 게 없어서 그런가 하고 찾아 봤더니
%% port search doxygen
doxygen @1.5.9 (textproc, devel)
Documentation system for several programming languages
Documentation system for several programming languages
있길래, 설치하고
%% sudo port install doxygen
실행 결과:
[#M_더보기|접기|
---> Fetching gmp
---> Attempting to fetch gmp-4.3.1.tar.bz2 from http://mirrors.kernel.org/gnu/gmp
---> Verifying checksum(s) for gmp
---> Extracting gmp
---> Applying patches to gmp
---> Configuring gmp
---> Building gmp
---> Staging gmp into destroot
---> Installing gmp @4.3.1_0
---> Activating gmp @4.3.1_0
---> Cleaning gmp
---> Fetching coreutils
---> Attempting to fetch coreutils-7.4.tar.gz from http://mirrors.kernel.org/gnu/coreutils
---> Verifying checksum(s) for coreutils
---> Extracting coreutils
---> Configuring coreutils
---> Building coreutils
---> Staging coreutils into destroot
---> Installing coreutils @7.4_0
---> Activating coreutils @7.4_0
---> Cleaning coreutils
---> Fetching automake
---> Attempting to fetch automake-1.11.tar.bz2 from http://mirrors.kernel.org/gnu/automake
---> Verifying checksum(s) for automake
---> Extracting automake
---> Configuring automake
---> Building automake
---> Staging automake into destroot
---> Installing automake @1.11_0
---> Activating automake @1.11_0
---> Cleaning automake
---> Fetching libtool
---> Attempting to fetch libtool-2.2.6a.tar.gz from http://distfiles.macports.org/libtool
---> Verifying checksum(s) for libtool
---> Extracting libtool
---> Configuring libtool
---> Building libtool
---> Staging libtool into destroot
---> Installing libtool @2.2.6a_0
---> Activating libtool @2.2.6a_0
---> Cleaning libtool
---> Fetching xpm
---> Attempting to fetch libXpm-3.5.7.tar.bz2 from http://distfiles.macports.org/xpm
---> Verifying checksum(s) for xpm
---> Extracting xpm
---> Configuring xpm
---> Building xpm
---> Staging xpm into destroot
---> Installing xpm @3.5.7_0
---> Activating xpm @3.5.7_0
---> Cleaning xpm
---> Fetching gd2
---> Attempting to fetch gd-2.0.35.tar.bz2 from http://distfiles.macports.org/gd2
---> Verifying checksum(s) for gd2
---> Extracting gd2
---> Applying patches to gd2
---> Configuring gd2
---> Building gd2
---> Staging gd2 into destroot
---> Installing gd2 @2.0.35_5
---> Activating gd2 @2.0.35_5
---> Cleaning gd2
---> Fetching urw-fonts
---> Attempting to fetch urw-fonts-1.0.7pre44.tar.bz2 from http://distfiles.macports.org/urw-fonts
---> Verifying checksum(s) for urw-fonts
---> Extracting urw-fonts
---> Configuring urw-fonts
---> Building urw-fonts
---> Staging urw-fonts into destroot
---> Installing urw-fonts @1.0.7pre44_0
---> Activating urw-fonts @1.0.7pre44_0
---> Cleaning urw-fonts
---> Fetching xorg-libice
---> Attempting to fetch libICE-1.0.5.tar.bz2 from http://distfiles.macports.org/xorg-libice
---> Verifying checksum(s) for xorg-libice
---> Extracting xorg-libice
---> Configuring xorg-libice
---> Building xorg-libice
---> Staging xorg-libice into destroot
---> Installing xorg-libice @1.0.5_0
---> Activating xorg-libice @1.0.5_0
---> Cleaning xorg-libice
---> Fetching xorg-libsm
---> Attempting to fetch libSM-1.1.0.tar.bz2 from http://www.x.org/pub/individual/lib/
---> Verifying checksum(s) for xorg-libsm
---> Extracting xorg-libsm
---> Configuring xorg-libsm
---> Building xorg-libsm
---> Staging xorg-libsm into destroot
---> Installing xorg-libsm @1.1.0_0
---> Activating xorg-libsm @1.1.0_0
---> Cleaning xorg-libsm
---> Fetching xorg-libXt
---> Attempting to fetch libXt-1.0.6.tar.bz2 from http://xorg.freedesktop.org/archive/individual/lib/
---> Verifying checksum(s) for xorg-libXt
---> Extracting xorg-libXt
---> Configuring xorg-libXt
---> Building xorg-libXt
---> Staging xorg-libXt into destroot
---> Installing xorg-libXt @1.0.6_0
---> Activating xorg-libXt @1.0.6_0
---> Cleaning xorg-libXt
---> Fetching xorg-libXmu
---> Attempting to fetch libXmu-1.0.4.tar.bz2 from http://distfiles.macports.org/xorg-libXmu
---> Verifying checksum(s) for xorg-libXmu
---> Extracting xorg-libXmu
---> Configuring xorg-libXmu
---> Building xorg-libXmu
---> Staging xorg-libXmu into destroot
---> Installing xorg-libXmu @1.0.4_0
---> Activating xorg-libXmu @1.0.4_0
---> Cleaning xorg-libXmu
---> Fetching xorg-libXaw
---> Attempting to fetch libXaw-1.0.6.tar.bz2 from http://distfiles.macports.org/xorg-libXaw
---> Verifying checksum(s) for xorg-libXaw
---> Extracting xorg-libXaw
---> Configuring xorg-libXaw
---> Building xorg-libXaw
---> Staging xorg-libXaw into destroot
---> Installing xorg-libXaw @1.0.6_0
---> Activating xorg-libXaw @1.0.6_0
---> Cleaning xorg-libXaw
---> Fetching graphviz
---> Attempting to fetch graphviz-2.24.0.tar.gz from http://distfiles.macports.org/graphviz
---> Verifying checksum(s) for graphviz
---> Extracting graphviz
---> Configuring graphviz
---> Building graphviz
---> Staging graphviz into destroot
---> Installing graphviz @2.24.0_0+macosx
---> Activating graphviz @2.24.0_0+macosx
---> Cleaning graphviz
---> Fetching doxygen
---> Attempting to fetch doxygen-1.5.9.src.tar.gz from http://distfiles.macports.org/doxygen
---> Verifying checksum(s) for doxygen
---> Extracting doxygen
---> Configuring doxygen
---> Building doxygen
---> Staging doxygen into destroot
---> Installing doxygen @1.5.9_0
---> Activating doxygen @1.5.9_0
---> Cleaning doxygen
---> Attempting to fetch gmp-4.3.1.tar.bz2 from http://mirrors.kernel.org/gnu/gmp
---> Verifying checksum(s) for gmp
---> Extracting gmp
---> Applying patches to gmp
---> Configuring gmp
---> Building gmp
---> Staging gmp into destroot
---> Installing gmp @4.3.1_0
---> Activating gmp @4.3.1_0
---> Cleaning gmp
---> Fetching coreutils
---> Attempting to fetch coreutils-7.4.tar.gz from http://mirrors.kernel.org/gnu/coreutils
---> Verifying checksum(s) for coreutils
---> Extracting coreutils
---> Configuring coreutils
---> Building coreutils
---> Staging coreutils into destroot
---> Installing coreutils @7.4_0
---> Activating coreutils @7.4_0
---> Cleaning coreutils
---> Fetching automake
---> Attempting to fetch automake-1.11.tar.bz2 from http://mirrors.kernel.org/gnu/automake
---> Verifying checksum(s) for automake
---> Extracting automake
---> Configuring automake
---> Building automake
---> Staging automake into destroot
---> Installing automake @1.11_0
---> Activating automake @1.11_0
---> Cleaning automake
---> Fetching libtool
---> Attempting to fetch libtool-2.2.6a.tar.gz from http://distfiles.macports.org/libtool
---> Verifying checksum(s) for libtool
---> Extracting libtool
---> Configuring libtool
---> Building libtool
---> Staging libtool into destroot
---> Installing libtool @2.2.6a_0
---> Activating libtool @2.2.6a_0
---> Cleaning libtool
---> Fetching xpm
---> Attempting to fetch libXpm-3.5.7.tar.bz2 from http://distfiles.macports.org/xpm
---> Verifying checksum(s) for xpm
---> Extracting xpm
---> Configuring xpm
---> Building xpm
---> Staging xpm into destroot
---> Installing xpm @3.5.7_0
---> Activating xpm @3.5.7_0
---> Cleaning xpm
---> Fetching gd2
---> Attempting to fetch gd-2.0.35.tar.bz2 from http://distfiles.macports.org/gd2
---> Verifying checksum(s) for gd2
---> Extracting gd2
---> Applying patches to gd2
---> Configuring gd2
---> Building gd2
---> Staging gd2 into destroot
---> Installing gd2 @2.0.35_5
---> Activating gd2 @2.0.35_5
---> Cleaning gd2
---> Fetching urw-fonts
---> Attempting to fetch urw-fonts-1.0.7pre44.tar.bz2 from http://distfiles.macports.org/urw-fonts
---> Verifying checksum(s) for urw-fonts
---> Extracting urw-fonts
---> Configuring urw-fonts
---> Building urw-fonts
---> Staging urw-fonts into destroot
---> Installing urw-fonts @1.0.7pre44_0
---> Activating urw-fonts @1.0.7pre44_0
---> Cleaning urw-fonts
---> Fetching xorg-libice
---> Attempting to fetch libICE-1.0.5.tar.bz2 from http://distfiles.macports.org/xorg-libice
---> Verifying checksum(s) for xorg-libice
---> Extracting xorg-libice
---> Configuring xorg-libice
---> Building xorg-libice
---> Staging xorg-libice into destroot
---> Installing xorg-libice @1.0.5_0
---> Activating xorg-libice @1.0.5_0
---> Cleaning xorg-libice
---> Fetching xorg-libsm
---> Attempting to fetch libSM-1.1.0.tar.bz2 from http://www.x.org/pub/individual/lib/
---> Verifying checksum(s) for xorg-libsm
---> Extracting xorg-libsm
---> Configuring xorg-libsm
---> Building xorg-libsm
---> Staging xorg-libsm into destroot
---> Installing xorg-libsm @1.1.0_0
---> Activating xorg-libsm @1.1.0_0
---> Cleaning xorg-libsm
---> Fetching xorg-libXt
---> Attempting to fetch libXt-1.0.6.tar.bz2 from http://xorg.freedesktop.org/archive/individual/lib/
---> Verifying checksum(s) for xorg-libXt
---> Extracting xorg-libXt
---> Configuring xorg-libXt
---> Building xorg-libXt
---> Staging xorg-libXt into destroot
---> Installing xorg-libXt @1.0.6_0
---> Activating xorg-libXt @1.0.6_0
---> Cleaning xorg-libXt
---> Fetching xorg-libXmu
---> Attempting to fetch libXmu-1.0.4.tar.bz2 from http://distfiles.macports.org/xorg-libXmu
---> Verifying checksum(s) for xorg-libXmu
---> Extracting xorg-libXmu
---> Configuring xorg-libXmu
---> Building xorg-libXmu
---> Staging xorg-libXmu into destroot
---> Installing xorg-libXmu @1.0.4_0
---> Activating xorg-libXmu @1.0.4_0
---> Cleaning xorg-libXmu
---> Fetching xorg-libXaw
---> Attempting to fetch libXaw-1.0.6.tar.bz2 from http://distfiles.macports.org/xorg-libXaw
---> Verifying checksum(s) for xorg-libXaw
---> Extracting xorg-libXaw
---> Configuring xorg-libXaw
---> Building xorg-libXaw
---> Staging xorg-libXaw into destroot
---> Installing xorg-libXaw @1.0.6_0
---> Activating xorg-libXaw @1.0.6_0
---> Cleaning xorg-libXaw
---> Fetching graphviz
---> Attempting to fetch graphviz-2.24.0.tar.gz from http://distfiles.macports.org/graphviz
---> Verifying checksum(s) for graphviz
---> Extracting graphviz
---> Configuring graphviz
---> Building graphviz
---> Staging graphviz into destroot
---> Installing graphviz @2.24.0_0+macosx
---> Activating graphviz @2.24.0_0+macosx
---> Cleaning graphviz
---> Fetching doxygen
---> Attempting to fetch doxygen-1.5.9.src.tar.gz from http://distfiles.macports.org/doxygen
---> Verifying checksum(s) for doxygen
---> Extracting doxygen
---> Configuring doxygen
---> Building doxygen
---> Staging doxygen into destroot
---> Installing doxygen @1.5.9_0
---> Activating doxygen @1.5.9_0
---> Cleaning doxygen
다시 시도했더니
%%% make docs
make: *** No rule to make target `docs'. Stop.
여전히 안 되는 듯... 아! doxygen을 맥포트로 설치해서 그런가 보다. (데이터베이스가 서로 다르다고 한다.)_M#]2-2-3. compile 컴파일하기
%%% make
실행 결과:
ga07087:libcvd lym$ make
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/cvd_timer.cc -o cvd_src/cvd_timer.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/diskbuffer2.cc -o cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.cc -o cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/exceptions.cc -o cvd_src/exceptions.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/image_io.cc -o cvd_src/image_io.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/bayer.cxx -o cvd_src/bayer.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/colourspace_convert.cxx -o cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/half_sample.cc -o cvd_src/half_sample.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/draw.cc -o cvd_src/draw.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/yuv422.cpp -o cvd_src/yuv422.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/yuv420.cpp -o cvd_src/yuv420.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/pnm_grok.cxx -o pnm_src/pnm_grok.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/bmp.cxx -o pnm_src/bmp.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/fits.cc -o pnm_src/fits.o
pnm_src/fits.cc:75: warning: 'bool get_bool(const std::string&)' defined but not used
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/save_postscript.cxx -o pnm_src/save_postscript.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/text_write.cc -o pnm_src/text_write.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/text.cxx -o pnm_src/text.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast_corner.cxx -o cvd_src/fast_corner.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/convolution.cc -o cvd_src/convolution.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.cxx -o cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.cc -o cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/videosource.cpp -o cvd_src/videosource.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/connected_components.cc -o cvd_src/connected_components.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.C -o cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.cc -o cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.cc -o cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/gradient.cc -o cvd_src/i686/gradient.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.cc -o cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.cc -o cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/utility_float.cc -o cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.cc -o cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.cc -o cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/slower_corner_7.cxx -o cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/slower_corner_8.cxx -o cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.cxx -o cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/slower_corner_11.cxx -o cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/faster_corner_9.cxx -o cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/faster_corner_10.cxx -o cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/faster_corner_12.cxx -o cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp -o cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o
cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp: In constructor 'CVD::QT::RawQT::RawQT(const CVD::ImageRef&, unsigned int, unsigned int, bool)':
cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp:171: warning: array subscript has type 'char'
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/synchronized.cpp -o cvd_src/synchronized.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/eventobject.cpp -o cvd_src/eventobject.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/thread.cpp -o cvd_src/thread.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.cc -o cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.cpp -o cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/videodisplay.cc -o cvd_src/videodisplay.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/glwindow.cc -o cvd_src/glwindow.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/gltext.cpp -o cvd_src/gltext.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/jpeg.cxx -o pnm_src/jpeg.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/tiff.cxx -o pnm_src/tiff.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/tiffwrite.cc -o pnm_src/tiffwrite.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/png.cc -o pnm_src/png.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/globlist.cxx -o cvd_src/globlist.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/tensor_voting.cc -o cvd_src/tensor_voting.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/brezenham.cc -o cvd_src/brezenham.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/draw_toon.cc -o cvd_src/draw_toon.o
ar crvs libcvd.a cvd_src/cvd_timer.o cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o cvd_src/exceptions.o cvd_src/image_io.o cvd_src/bayer.o cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o cvd_src/half_sample.o cvd_src/draw.o cvd_src/yuv422.o cvd_src/yuv420.o pnm_src/pnm_grok.o pnm_src/bmp.o pnm_src/fits.o pnm_src/save_postscript.o pnm_src/text_write.o pnm_src/text.o cvd_src/fast_corner.o cvd_src/convolution.o cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o cvd_src/videosource.o cvd_src/connected_components.o cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o cvd_src/i686/gradient.o cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o cvd_src/synchronized.o cvd_src/eventobject.o cvd_src/thread.o cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o cvd_src/videodisplay.o cvd_src/glwindow.o cvd_src/gltext.o pnm_src/jpeg.o pnm_src/tiff.o pnm_src/tiffwrite.o pnm_src/png.o cvd_src/globlist.o cvd_src/tensor_voting.o cvd_src/brezenham.o cvd_src/draw_toon.o
a - cvd_src/cvd_timer.o
a - cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o
a - cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o
a - cvd_src/exceptions.o
a - cvd_src/image_io.o
a - cvd_src/bayer.o
a - cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o
a - cvd_src/half_sample.o
a - cvd_src/draw.o
a - cvd_src/yuv422.o
a - cvd_src/yuv420.o
a - pnm_src/pnm_grok.o
a - pnm_src/bmp.o
a - pnm_src/fits.o
a - pnm_src/save_postscript.o
a - pnm_src/text_write.o
a - pnm_src/text.o
a - cvd_src/fast_corner.o
a - cvd_src/convolution.o
a - cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o
a - cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o
a - cvd_src/videosource.o
a - cvd_src/connected_components.o
a - cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o
a - cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o
a - cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o
a - cvd_src/i686/gradient.o
a - cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o
a - cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o
a - cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o
a - cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o
a - cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o
a - cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o
a - cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o
a - cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o
a - cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o
a - cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o
a - cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o
a - cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o
a - cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o
a - cvd_src/synchronized.o
a - cvd_src/eventobject.o
a - cvd_src/thread.o
a - cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o
a - cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o
a - cvd_src/videodisplay.o
a - cvd_src/glwindow.o
a - cvd_src/gltext.o
a - pnm_src/jpeg.o
a - pnm_src/tiff.o
a - pnm_src/tiffwrite.o
a - pnm_src/png.o
a - cvd_src/globlist.o
a - cvd_src/tensor_voting.o
a - cvd_src/brezenham.o
a - cvd_src/draw_toon.o
ranlib libcvd.a
rm -f libcvd.dylib libcvd-0.dylib libcvd-0.7.dylib
g++ -dynamiclib -o libcvd-0.7.dylib cvd_src/cvd_timer.o cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o cvd_src/exceptions.o cvd_src/image_io.o cvd_src/bayer.o cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o cvd_src/half_sample.o cvd_src/draw.o cvd_src/yuv422.o cvd_src/yuv420.o pnm_src/pnm_grok.o pnm_src/bmp.o pnm_src/fits.o pnm_src/save_postscript.o pnm_src/text_write.o pnm_src/text.o cvd_src/fast_corner.o cvd_src/convolution.o cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o cvd_src/videosource.o cvd_src/connected_components.o cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o cvd_src/i686/gradient.o cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o cvd_src/synchronized.o cvd_src/eventobject.o cvd_src/thread.o cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o cvd_src/videodisplay.o cvd_src/glwindow.o cvd_src/gltext.o pnm_src/jpeg.o pnm_src/tiff.o pnm_src/tiffwrite.o pnm_src/png.o cvd_src/globlist.o cvd_src/tensor_voting.o cvd_src/brezenham.o cvd_src/draw_toon.o -L. -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
ln -s libcvd-0.7.dylib libcvd-0.dylib
ln -s libcvd-0.dylib libcvd.dylib
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/se3_exp.cxx -o progs/se3_exp.o
g++ -o progs/se3_exp progs/se3_exp.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/se3_ln.cxx -o progs/se3_ln.o
g++ -o progs/se3_ln progs/se3_ln.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/se3_pre_mul.cxx -o progs/se3_pre_mul.o
g++ -o progs/se3_pre_mul progs/se3_pre_mul.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/se3_post_mul.cxx -o progs/se3_post_mul.o
g++ -o progs/se3_post_mul progs/se3_post_mul.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/se3_inv.cxx -o progs/se3_inv.o
g++ -o progs/se3_inv progs/se3_inv.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/calibrate.cxx -o progs/calibrate.o
g++ -o progs/calibrate progs/calibrate.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/img_play.cxx -o progs/img_play.o
g++ -o progs/img_play progs/img_play.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/cvd_display_image.cxx -o progs/cvd_display_image.o
g++ -o progs/cvd_display_image progs/cvd_display_image.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/img_play_bw.cxx -o progs/img_play_bw.o
g++ -o progs/img_play_bw progs/img_play_bw.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/img_play_deinterlace.cxx -o progs/img_play_deinterlace.o
g++ -o progs/img_play_deinterlace progs/img_play_deinterlace.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/video_play_source.cc -o progs/video_play_source.o
g++ -o progs/video_play_source progs/video_play_source.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
mkdir -p debug/cvd_src debug/cvd_src/IRIX debug/cvd_src/Linux debug/cvd_src/OSX debug/cvd_src/fast debug/cvd_src/i686 debug/cvd_src/noarch debug/pnm_src debug/cvd_src/thread debug/cvd_src/nothread
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/cvd_timer.cc -o debug/cvd_src/cvd_timer.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/diskbuffer2.cc -o debug/cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.cc -o debug/cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/exceptions.cc -o debug/cvd_src/exceptions.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/image_io.cc -o debug/cvd_src/image_io.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/bayer.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/bayer.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/colourspace_convert.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/half_sample.cc -o debug/cvd_src/half_sample.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/draw.cc -o debug/cvd_src/draw.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/yuv422.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/yuv422.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/yuv420.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/yuv420.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/pnm_grok.cxx -o debug/pnm_src/pnm_grok.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/bmp.cxx -o debug/pnm_src/bmp.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/fits.cc -o debug/pnm_src/fits.o
pnm_src/fits.cc:75: warning: 'bool get_bool(const std::string&)' defined but not used
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/save_postscript.cxx -o debug/pnm_src/save_postscript.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/text_write.cc -o debug/pnm_src/text_write.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/text.cxx -o debug/pnm_src/text.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast_corner.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast_corner.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/convolution.cc -o debug/cvd_src/convolution.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.cc -o debug/cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/videosource.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/videosource.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/connected_components.cc -o debug/cvd_src/connected_components.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.C -o debug/cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.cc -o debug/cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.cc -o debug/cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/gradient.cc -o debug/cvd_src/i686/gradient.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.cc -o debug/cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.cc -o debug/cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/utility_float.cc -o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.cc -o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.cc -o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/slower_corner_7.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/slower_corner_8.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/slower_corner_11.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/faster_corner_9.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/faster_corner_10.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/faster_corner_12.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o
cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp: In constructor 'CVD::QT::RawQT::RawQT(const CVD::ImageRef&, unsigned int, unsigned int, bool)':
cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp:171: warning: array subscript has type 'char'
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/synchronized.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/synchronized.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/eventobject.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/eventobject.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/thread.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/thread.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.cc -o debug/cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/videodisplay.cc -o debug/cvd_src/videodisplay.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/glwindow.cc -o debug/cvd_src/glwindow.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/gltext.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/gltext.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/jpeg.cxx -o debug/pnm_src/jpeg.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/tiff.cxx -o debug/pnm_src/tiff.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/tiffwrite.cc -o debug/pnm_src/tiffwrite.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/png.cc -o debug/pnm_src/png.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/globlist.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/globlist.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/tensor_voting.cc -o debug/cvd_src/tensor_voting.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/brezenham.cc -o debug/cvd_src/brezenham.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/draw_toon.cc -o debug/cvd_src/draw_toon.o
ar crvs libcvd_debug.a debug/cvd_src/cvd_timer.o debug/cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o debug/cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o debug/cvd_src/exceptions.o debug/cvd_src/image_io.o debug/cvd_src/bayer.o debug/cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o debug/cvd_src/half_sample.o debug/cvd_src/draw.o debug/cvd_src/yuv422.o debug/cvd_src/yuv420.o debug/pnm_src/pnm_grok.o debug/pnm_src/bmp.o debug/pnm_src/fits.o debug/pnm_src/save_postscript.o debug/pnm_src/text_write.o debug/pnm_src/text.o debug/cvd_src/fast_corner.o debug/cvd_src/convolution.o debug/cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o debug/cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o debug/cvd_src/videosource.o debug/cvd_src/connected_components.o debug/cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o debug/cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o debug/cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o debug/cvd_src/i686/gradient.o debug/cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o debug/cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o debug/cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o debug/cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o debug/cvd_src/synchronized.o debug/cvd_src/eventobject.o debug/cvd_src/thread.o debug/cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o debug/cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o debug/cvd_src/videodisplay.o debug/cvd_src/glwindow.o debug/cvd_src/gltext.o debug/pnm_src/jpeg.o debug/pnm_src/tiff.o debug/pnm_src/tiffwrite.o debug/pnm_src/png.o debug/cvd_src/globlist.o debug/cvd_src/tensor_voting.o debug/cvd_src/brezenham.o debug/cvd_src/draw_toon.o
a - debug/cvd_src/cvd_timer.o
a - debug/cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o
a - debug/cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o
a - debug/cvd_src/exceptions.o
a - debug/cvd_src/image_io.o
a - debug/cvd_src/bayer.o
a - debug/cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o
a - debug/cvd_src/half_sample.o
a - debug/cvd_src/draw.o
a - debug/cvd_src/yuv422.o
a - debug/cvd_src/yuv420.o
a - debug/pnm_src/pnm_grok.o
a - debug/pnm_src/bmp.o
a - debug/pnm_src/fits.o
a - debug/pnm_src/save_postscript.o
a - debug/pnm_src/text_write.o
a - debug/pnm_src/text.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast_corner.o
a - debug/cvd_src/convolution.o
a - debug/cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o
a - debug/cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o
a - debug/cvd_src/videosource.o
a - debug/cvd_src/connected_components.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o
a - debug/cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/gradient.o
a - debug/cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o
a - debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o
a - debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o
a - debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o
a - debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o
a - debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o
a - debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o
a - debug/cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o
a - debug/cvd_src/synchronized.o
a - debug/cvd_src/eventobject.o
a - debug/cvd_src/thread.o
a - debug/cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o
a - debug/cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o
a - debug/cvd_src/videodisplay.o
a - debug/cvd_src/glwindow.o
a - debug/cvd_src/gltext.o
a - debug/pnm_src/jpeg.o
a - debug/pnm_src/tiff.o
a - debug/pnm_src/tiffwrite.o
a - debug/pnm_src/png.o
a - debug/cvd_src/globlist.o
a - debug/cvd_src/tensor_voting.o
a - debug/cvd_src/brezenham.o
a - debug/cvd_src/draw_toon.o
ranlib libcvd_debug.a
rm -f libcvd_debug.dylib libcvd_debug-0.dylib libcvd_debug-0.7.dylib
g++ -dynamiclib -o libcvd_debug-0.7.dylib debug/cvd_src/cvd_timer.o debug/cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o debug/cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o debug/cvd_src/exceptions.o debug/cvd_src/image_io.o debug/cvd_src/bayer.o debug/cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o debug/cvd_src/half_sample.o debug/cvd_src/draw.o debug/cvd_src/yuv422.o debug/cvd_src/yuv420.o debug/pnm_src/pnm_grok.o debug/pnm_src/bmp.o debug/pnm_src/fits.o debug/pnm_src/save_postscript.o debug/pnm_src/text_write.o debug/pnm_src/text.o debug/cvd_src/fast_corner.o debug/cvd_src/convolution.o debug/cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o debug/cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o debug/cvd_src/videosource.o debug/cvd_src/connected_components.o debug/cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o debug/cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o debug/cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o debug/cvd_src/i686/gradient.o debug/cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o debug/cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o debug/cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o debug/cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o debug/cvd_src/synchronized.o debug/cvd_src/eventobject.o debug/cvd_src/thread.o debug/cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o debug/cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o debug/cvd_src/videodisplay.o debug/cvd_src/glwindow.o debug/cvd_src/gltext.o debug/pnm_src/jpeg.o debug/pnm_src/tiff.o debug/pnm_src/tiffwrite.o debug/pnm_src/png.o debug/cvd_src/globlist.o debug/cvd_src/tensor_voting.o debug/cvd_src/brezenham.o debug/cvd_src/draw_toon.o -L. -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
ln -s libcvd_debug-0.7.dylib libcvd_debug-0.dylib
ln -s libcvd_debug-0.dylib libcvd_debug.dylib
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/cvd_timer.cc -o cvd_src/cvd_timer.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/diskbuffer2.cc -o cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.cc -o cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/exceptions.cc -o cvd_src/exceptions.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/image_io.cc -o cvd_src/image_io.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/bayer.cxx -o cvd_src/bayer.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/colourspace_convert.cxx -o cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/half_sample.cc -o cvd_src/half_sample.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/draw.cc -o cvd_src/draw.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/yuv422.cpp -o cvd_src/yuv422.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/yuv420.cpp -o cvd_src/yuv420.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/pnm_grok.cxx -o pnm_src/pnm_grok.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/bmp.cxx -o pnm_src/bmp.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/fits.cc -o pnm_src/fits.o
pnm_src/fits.cc:75: warning: 'bool get_bool(const std::string&)' defined but not used
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/save_postscript.cxx -o pnm_src/save_postscript.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/text_write.cc -o pnm_src/text_write.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/text.cxx -o pnm_src/text.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast_corner.cxx -o cvd_src/fast_corner.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/convolution.cc -o cvd_src/convolution.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.cxx -o cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.cc -o cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/videosource.cpp -o cvd_src/videosource.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/connected_components.cc -o cvd_src/connected_components.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.C -o cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.cc -o cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.cc -o cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/gradient.cc -o cvd_src/i686/gradient.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.cc -o cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.cc -o cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/utility_float.cc -o cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.cc -o cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.cc -o cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/slower_corner_7.cxx -o cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/slower_corner_8.cxx -o cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.cxx -o cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/slower_corner_11.cxx -o cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.cxx -o cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/faster_corner_9.cxx -o cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/faster_corner_10.cxx -o cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/faster_corner_12.cxx -o cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp -o cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o
cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp: In constructor 'CVD::QT::RawQT::RawQT(const CVD::ImageRef&, unsigned int, unsigned int, bool)':
cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp:171: warning: array subscript has type 'char'
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/synchronized.cpp -o cvd_src/synchronized.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/eventobject.cpp -o cvd_src/eventobject.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/thread.cpp -o cvd_src/thread.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.cc -o cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.cpp -o cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/videodisplay.cc -o cvd_src/videodisplay.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/glwindow.cc -o cvd_src/glwindow.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/gltext.cpp -o cvd_src/gltext.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/jpeg.cxx -o pnm_src/jpeg.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/tiff.cxx -o pnm_src/tiff.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/tiffwrite.cc -o pnm_src/tiffwrite.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c pnm_src/png.cc -o pnm_src/png.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/globlist.cxx -o cvd_src/globlist.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/tensor_voting.cc -o cvd_src/tensor_voting.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/brezenham.cc -o cvd_src/brezenham.o
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c cvd_src/draw_toon.cc -o cvd_src/draw_toon.o
ar crvs libcvd.a cvd_src/cvd_timer.o cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o cvd_src/exceptions.o cvd_src/image_io.o cvd_src/bayer.o cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o cvd_src/half_sample.o cvd_src/draw.o cvd_src/yuv422.o cvd_src/yuv420.o pnm_src/pnm_grok.o pnm_src/bmp.o pnm_src/fits.o pnm_src/save_postscript.o pnm_src/text_write.o pnm_src/text.o cvd_src/fast_corner.o cvd_src/convolution.o cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o cvd_src/videosource.o cvd_src/connected_components.o cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o cvd_src/i686/gradient.o cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o cvd_src/synchronized.o cvd_src/eventobject.o cvd_src/thread.o cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o cvd_src/videodisplay.o cvd_src/glwindow.o cvd_src/gltext.o pnm_src/jpeg.o pnm_src/tiff.o pnm_src/tiffwrite.o pnm_src/png.o cvd_src/globlist.o cvd_src/tensor_voting.o cvd_src/brezenham.o cvd_src/draw_toon.o
a - cvd_src/cvd_timer.o
a - cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o
a - cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o
a - cvd_src/exceptions.o
a - cvd_src/image_io.o
a - cvd_src/bayer.o
a - cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o
a - cvd_src/half_sample.o
a - cvd_src/draw.o
a - cvd_src/yuv422.o
a - cvd_src/yuv420.o
a - pnm_src/pnm_grok.o
a - pnm_src/bmp.o
a - pnm_src/fits.o
a - pnm_src/save_postscript.o
a - pnm_src/text_write.o
a - pnm_src/text.o
a - cvd_src/fast_corner.o
a - cvd_src/convolution.o
a - cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o
a - cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o
a - cvd_src/videosource.o
a - cvd_src/connected_components.o
a - cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o
a - cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o
a - cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o
a - cvd_src/i686/gradient.o
a - cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o
a - cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o
a - cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o
a - cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o
a - cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o
a - cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o
a - cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o
a - cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o
a - cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o
a - cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o
a - cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o
a - cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o
a - cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o
a - cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o
a - cvd_src/synchronized.o
a - cvd_src/eventobject.o
a - cvd_src/thread.o
a - cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o
a - cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o
a - cvd_src/videodisplay.o
a - cvd_src/glwindow.o
a - cvd_src/gltext.o
a - pnm_src/jpeg.o
a - pnm_src/tiff.o
a - pnm_src/tiffwrite.o
a - pnm_src/png.o
a - cvd_src/globlist.o
a - cvd_src/tensor_voting.o
a - cvd_src/brezenham.o
a - cvd_src/draw_toon.o
ranlib libcvd.a
rm -f libcvd.dylib libcvd-0.dylib libcvd-0.7.dylib
g++ -dynamiclib -o libcvd-0.7.dylib cvd_src/cvd_timer.o cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o cvd_src/exceptions.o cvd_src/image_io.o cvd_src/bayer.o cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o cvd_src/half_sample.o cvd_src/draw.o cvd_src/yuv422.o cvd_src/yuv420.o pnm_src/pnm_grok.o pnm_src/bmp.o pnm_src/fits.o pnm_src/save_postscript.o pnm_src/text_write.o pnm_src/text.o cvd_src/fast_corner.o cvd_src/convolution.o cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o cvd_src/videosource.o cvd_src/connected_components.o cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o cvd_src/i686/gradient.o cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o cvd_src/synchronized.o cvd_src/eventobject.o cvd_src/thread.o cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o cvd_src/videodisplay.o cvd_src/glwindow.o cvd_src/gltext.o pnm_src/jpeg.o pnm_src/tiff.o pnm_src/tiffwrite.o pnm_src/png.o cvd_src/globlist.o cvd_src/tensor_voting.o cvd_src/brezenham.o cvd_src/draw_toon.o -L. -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
ln -s libcvd-0.7.dylib libcvd-0.dylib
ln -s libcvd-0.dylib libcvd.dylib
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/se3_exp.cxx -o progs/se3_exp.o
g++ -o progs/se3_exp progs/se3_exp.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/se3_ln.cxx -o progs/se3_ln.o
g++ -o progs/se3_ln progs/se3_ln.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/se3_pre_mul.cxx -o progs/se3_pre_mul.o
g++ -o progs/se3_pre_mul progs/se3_pre_mul.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/se3_post_mul.cxx -o progs/se3_post_mul.o
g++ -o progs/se3_post_mul progs/se3_post_mul.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/se3_inv.cxx -o progs/se3_inv.o
g++ -o progs/se3_inv progs/se3_inv.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/calibrate.cxx -o progs/calibrate.o
g++ -o progs/calibrate progs/calibrate.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/img_play.cxx -o progs/img_play.o
g++ -o progs/img_play progs/img_play.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/cvd_display_image.cxx -o progs/cvd_display_image.o
g++ -o progs/cvd_display_image progs/cvd_display_image.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/img_play_bw.cxx -o progs/img_play_bw.o
g++ -o progs/img_play_bw progs/img_play_bw.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/img_play_deinterlace.cxx -o progs/img_play_deinterlace.o
g++ -o progs/img_play_deinterlace progs/img_play_deinterlace.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
g++ -O3 -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -c progs/video_play_source.cc -o progs/video_play_source.o
g++ -o progs/video_play_source progs/video_play_source.o -L. -lcvd -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
mkdir -p debug/cvd_src debug/cvd_src/IRIX debug/cvd_src/Linux debug/cvd_src/OSX debug/cvd_src/fast debug/cvd_src/i686 debug/cvd_src/noarch debug/pnm_src debug/cvd_src/thread debug/cvd_src/nothread
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/cvd_timer.cc -o debug/cvd_src/cvd_timer.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/diskbuffer2.cc -o debug/cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.cc -o debug/cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/exceptions.cc -o debug/cvd_src/exceptions.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/image_io.cc -o debug/cvd_src/image_io.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/bayer.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/bayer.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/colourspace_convert.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/half_sample.cc -o debug/cvd_src/half_sample.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/draw.cc -o debug/cvd_src/draw.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/yuv422.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/yuv422.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/yuv420.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/yuv420.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/pnm_grok.cxx -o debug/pnm_src/pnm_grok.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/bmp.cxx -o debug/pnm_src/bmp.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/fits.cc -o debug/pnm_src/fits.o
pnm_src/fits.cc:75: warning: 'bool get_bool(const std::string&)' defined but not used
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/save_postscript.cxx -o debug/pnm_src/save_postscript.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/text_write.cc -o debug/pnm_src/text_write.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/text.cxx -o debug/pnm_src/text.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast_corner.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast_corner.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/convolution.cc -o debug/cvd_src/convolution.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.cc -o debug/cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/videosource.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/videosource.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/connected_components.cc -o debug/cvd_src/connected_components.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.C -o debug/cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.cc -o debug/cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.cc -o debug/cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/gradient.cc -o debug/cvd_src/i686/gradient.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.cc -o debug/cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.cc -o debug/cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/utility_float.cc -o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.cc -o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.cc -o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/slower_corner_7.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/slower_corner_8.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/slower_corner_11.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/faster_corner_9.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/faster_corner_10.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/faster_corner_12.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o
cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp: In constructor 'CVD::QT::RawQT::RawQT(const CVD::ImageRef&, unsigned int, unsigned int, bool)':
cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.cpp:171: warning: array subscript has type 'char'
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/synchronized.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/synchronized.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/eventobject.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/eventobject.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/thread.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/thread.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.cc -o debug/cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/videodisplay.cc -o debug/cvd_src/videodisplay.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/glwindow.cc -o debug/cvd_src/glwindow.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/gltext.cpp -o debug/cvd_src/gltext.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/jpeg.cxx -o debug/pnm_src/jpeg.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/tiff.cxx -o debug/pnm_src/tiff.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/tiffwrite.cc -o debug/pnm_src/tiffwrite.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c pnm_src/png.cc -o debug/pnm_src/png.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/globlist.cxx -o debug/cvd_src/globlist.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/tensor_voting.cc -o debug/cvd_src/tensor_voting.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/brezenham.cc -o debug/cvd_src/brezenham.o
g++ -I. -I. -INONE/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pipe -ggdb -fPIC -mmmx -msse -msse -msse2 -msse3 -I/usr/X11/include -pthread -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG -DCVD_IMAGE_DEBUG -c cvd_src/draw_toon.cc -o debug/cvd_src/draw_toon.o
ar crvs libcvd_debug.a debug/cvd_src/cvd_timer.o debug/cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o debug/cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o debug/cvd_src/exceptions.o debug/cvd_src/image_io.o debug/cvd_src/bayer.o debug/cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o debug/cvd_src/half_sample.o debug/cvd_src/draw.o debug/cvd_src/yuv422.o debug/cvd_src/yuv420.o debug/pnm_src/pnm_grok.o debug/pnm_src/bmp.o debug/pnm_src/fits.o debug/pnm_src/save_postscript.o debug/pnm_src/text_write.o debug/pnm_src/text.o debug/cvd_src/fast_corner.o debug/cvd_src/convolution.o debug/cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o debug/cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o debug/cvd_src/videosource.o debug/cvd_src/connected_components.o debug/cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o debug/cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o debug/cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o debug/cvd_src/i686/gradient.o debug/cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o debug/cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o debug/cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o debug/cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o debug/cvd_src/synchronized.o debug/cvd_src/eventobject.o debug/cvd_src/thread.o debug/cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o debug/cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o debug/cvd_src/videodisplay.o debug/cvd_src/glwindow.o debug/cvd_src/gltext.o debug/pnm_src/jpeg.o debug/pnm_src/tiff.o debug/pnm_src/tiffwrite.o debug/pnm_src/png.o debug/cvd_src/globlist.o debug/cvd_src/tensor_voting.o debug/cvd_src/brezenham.o debug/cvd_src/draw_toon.o
a - debug/cvd_src/cvd_timer.o
a - debug/cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o
a - debug/cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o
a - debug/cvd_src/exceptions.o
a - debug/cvd_src/image_io.o
a - debug/cvd_src/bayer.o
a - debug/cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o
a - debug/cvd_src/half_sample.o
a - debug/cvd_src/draw.o
a - debug/cvd_src/yuv422.o
a - debug/cvd_src/yuv420.o
a - debug/pnm_src/pnm_grok.o
a - debug/pnm_src/bmp.o
a - debug/pnm_src/fits.o
a - debug/pnm_src/save_postscript.o
a - debug/pnm_src/text_write.o
a - debug/pnm_src/text.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast_corner.o
a - debug/cvd_src/convolution.o
a - debug/cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o
a - debug/cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o
a - debug/cvd_src/videosource.o
a - debug/cvd_src/connected_components.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o
a - debug/cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/gradient.o
a - debug/cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o
a - debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o
a - debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o
a - debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o
a - debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o
a - debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o
a - debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o
a - debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o
a - debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o
a - debug/cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o
a - debug/cvd_src/synchronized.o
a - debug/cvd_src/eventobject.o
a - debug/cvd_src/thread.o
a - debug/cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o
a - debug/cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o
a - debug/cvd_src/videodisplay.o
a - debug/cvd_src/glwindow.o
a - debug/cvd_src/gltext.o
a - debug/pnm_src/jpeg.o
a - debug/pnm_src/tiff.o
a - debug/pnm_src/tiffwrite.o
a - debug/pnm_src/png.o
a - debug/cvd_src/globlist.o
a - debug/cvd_src/tensor_voting.o
a - debug/cvd_src/brezenham.o
a - debug/cvd_src/draw_toon.o
ranlib libcvd_debug.a
rm -f libcvd_debug.dylib libcvd_debug-0.dylib libcvd_debug-0.7.dylib
g++ -dynamiclib -o libcvd_debug-0.7.dylib debug/cvd_src/cvd_timer.o debug/cvd_src/diskbuffer2.o debug/cvd_src/deinterlacebuffer.o debug/cvd_src/exceptions.o debug/cvd_src/image_io.o debug/cvd_src/bayer.o debug/cvd_src/colourspace_convert.o debug/cvd_src/half_sample.o debug/cvd_src/draw.o debug/cvd_src/yuv422.o debug/cvd_src/yuv420.o debug/pnm_src/pnm_grok.o debug/pnm_src/bmp.o debug/pnm_src/fits.o debug/pnm_src/save_postscript.o debug/pnm_src/text_write.o debug/pnm_src/text.o debug/cvd_src/fast_corner.o debug/cvd_src/convolution.o debug/cvd_src/nonmax_suppression.o debug/cvd_src/timeddiskbuffer.o debug/cvd_src/videosource.o debug/cvd_src/connected_components.o debug/cvd_src/i686/yuv411_to_stuff_MMX.o debug/cvd_src/noarch/convert_rgb_to_y.o debug/cvd_src/i686/convolve_gaussian.o debug/cvd_src/i686/gradient.o debug/cvd_src/noarch/yuv422_wrapper.o debug/cvd_src/i686/median_3x3.o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_float.o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_byte_differences.o debug/cvd_src/i686/utility_double_int.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_7_score.o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_7.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_8_score.o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_8.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_9_score.o debug/cvd_src/fast_corner_9_nonmax.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_10_score.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_11_score.o debug/cvd_src/slower_corner_11.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_detect.o debug/cvd_src/fast/fast_12_score.o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_9.o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_10.o debug/cvd_src/faster_corner_12.o debug/cvd_src/OSX/qtbuffer.o debug/cvd_src/synchronized.o debug/cvd_src/eventobject.o debug/cvd_src/thread.o debug/cvd_src/thread/runnable_batch.o debug/cvd_src/noarch/default_memalign.o debug/cvd_src/videodisplay.o debug/cvd_src/glwindow.o debug/cvd_src/gltext.o debug/pnm_src/jpeg.o debug/pnm_src/tiff.o debug/pnm_src/tiffwrite.o debug/pnm_src/png.o debug/cvd_src/globlist.o debug/cvd_src/tensor_voting.o debug/cvd_src/brezenham.o debug/cvd_src/draw_toon.o -L. -ltiff -ljpeg -lpng -lGLU -lGL -L/opt/local/lib -framework Carbon -framework QuickTime -L/usr/X11/lib -lX11 -lXext -dylib_file /System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib:/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Libraries/libGL.dylib -framework Accelerate -pthread
ln -s libcvd_debug-0.7.dylib libcvd_debug-0.dylib
ln -s libcvd_debug-0.dylib libcvd_debug.dylib
2-2-4. install 설치하기
%%% sudo make install
실행 결과:
mkdir -p /usr/local/bin
[ "progs/se3_exp progs/se3_ln progs/se3_pre_mul progs/se3_post_mul progs/se3_inv progs/calibrate progs/img_play progs/cvd_display_image progs/img_play_bw progs/img_play_deinterlace progs/video_play_source " = "" ] || cp progs/se3_exp progs/se3_ln progs/se3_pre_mul progs/se3_post_mul progs/se3_inv progs/calibrate progs/img_play progs/cvd_display_image progs/img_play_bw progs/img_play_deinterlace progs/video_play_source /usr/local/bin
mkdir -p /usr/local/include
cp -r cvd /usr/local/include
mkdir -p /usr/local/lib
cp libcvd-0.7.dylib /usr/local/lib
rm -f /usr/local/lib/libcvd-0.dylib /usr/local/lib/libcvd.dylib
ln -s /usr/local/lib/libcvd-0.7.dylib /usr/local/lib/libcvd-0.dylib
ln -s /usr/local/lib/libcvd-0.dylib /usr/local/lib/libcvd.dylib
mkdir -p /usr/local/lib
cp libcvd.a /usr/local/lib
mkdir -p /usr/local/lib
cp libcvd_debug-0.7.dylib /usr/local/lib
rm -f /usr/local/lib/libcvd_debug-0.dylib /usr/local/lib/libcvd_debug.dylib
ln -s /usr/local/lib/libcvd_debug-0.7.dylib /usr/local/lib/libcvd_debug-0.dylib
ln -s /usr/local/lib/libcvd_debug-0.dylib /usr/local/lib/libcvd_debug.dylib
cp libcvd_debug.a /usr/local/lib
[ "progs/se3_exp progs/se3_ln progs/se3_pre_mul progs/se3_post_mul progs/se3_inv progs/calibrate progs/img_play progs/cvd_display_image progs/img_play_bw progs/img_play_deinterlace progs/video_play_source " = "" ] || cp progs/se3_exp progs/se3_ln progs/se3_pre_mul progs/se3_post_mul progs/se3_inv progs/calibrate progs/img_play progs/cvd_display_image progs/img_play_bw progs/img_play_deinterlace progs/video_play_source /usr/local/bin
mkdir -p /usr/local/include
cp -r cvd /usr/local/include
mkdir -p /usr/local/lib
cp libcvd-0.7.dylib /usr/local/lib
rm -f /usr/local/lib/libcvd-0.dylib /usr/local/lib/libcvd.dylib
ln -s /usr/local/lib/libcvd-0.7.dylib /usr/local/lib/libcvd-0.dylib
ln -s /usr/local/lib/libcvd-0.dylib /usr/local/lib/libcvd.dylib
mkdir -p /usr/local/lib
cp libcvd.a /usr/local/lib
mkdir -p /usr/local/lib
cp libcvd_debug-0.7.dylib /usr/local/lib
rm -f /usr/local/lib/libcvd_debug-0.dylib /usr/local/lib/libcvd_debug.dylib
ln -s /usr/local/lib/libcvd_debug-0.7.dylib /usr/local/lib/libcvd_debug-0.dylib
ln -s /usr/local/lib/libcvd_debug-0.dylib /usr/local/lib/libcvd_debug.dylib
cp libcvd_debug.a /usr/local/lib
2-3. Gvars3 설치
2-3-1. configure 파일 실행
Gvars3 폴더에 들어가서
%%% ./configure --disable-widgets
실행 결과:
checking for gawk... no
checking for mawk... no
checking for nawk... no
checking for awk... awk
checking for g++... g++
checking for C++ compiler default output file name... a.out
checking whether the C++ compiler works... yes
checking whether we are cross compiling... no
checking for suffix of executables...
checking for suffix of object files... o
checking whether we are using the GNU C++ compiler... yes
checking whether g++ accepts -g... yes
checking how to run the C++ preprocessor... g++ -E
checking for grep that handles long lines and -e... /usr/bin/grep
checking for egrep... /usr/bin/grep -E
checking for ANSI C header files... yes
checking for sys/types.h... yes
checking for sys/stat.h... yes
checking for stdlib.h... yes
checking for string.h... yes
checking for memory.h... yes
checking for strings.h... yes
checking for inttypes.h... yes
checking for stdint.h... yes
checking for unistd.h... yes
checking iostream usability... yes
checking iostream presence... yes
checking for iostream... yes
checking build system type... i386-apple-darwin9.7.0
checking host system type... i386-apple-darwin9.7.0
configure: Adding /sw to the build path.
configure: Adding /opt/local to the build path.
checking if compiler flag -Wall works... yes
checking if compiler flag -Wextra works... yes
--------------------------
Checking for options
--------------------------
checking for TooN... yes
checking for TooN-2... yes
checking if compiler flag -pthread works... yes
checking for rl_done in -lreadline... yes
------------------------------------------------
Checking for widget libraries (provides GUI_...)
------------------------------------------------
configure: WARNING: No GUI functionality enabled
Options:
toon readline
Missing options:
gui
GUI support:
none
configure: creating ./config.status
config.status: creating Makefile
config.status: creating gvars3/config.h
checking for mawk... no
checking for nawk... no
checking for awk... awk
checking for g++... g++
checking for C++ compiler default output file name... a.out
checking whether the C++ compiler works... yes
checking whether we are cross compiling... no
checking for suffix of executables...
checking for suffix of object files... o
checking whether we are using the GNU C++ compiler... yes
checking whether g++ accepts -g... yes
checking how to run the C++ preprocessor... g++ -E
checking for grep that handles long lines and -e... /usr/bin/grep
checking for egrep... /usr/bin/grep -E
checking for ANSI C header files... yes
checking for sys/types.h... yes
checking for sys/stat.h... yes
checking for stdlib.h... yes
checking for string.h... yes
checking for memory.h... yes
checking for strings.h... yes
checking for inttypes.h... yes
checking for stdint.h... yes
checking for unistd.h... yes
checking iostream usability... yes
checking iostream presence... yes
checking for iostream... yes
checking build system type... i386-apple-darwin9.7.0
checking host system type... i386-apple-darwin9.7.0
configure: Adding /sw to the build path.
configure: Adding /opt/local to the build path.
checking if compiler flag -Wall works... yes
checking if compiler flag -Wextra works... yes
--------------------------
Checking for options
--------------------------
checking for TooN... yes
checking for TooN-2... yes
checking if compiler flag -pthread works... yes
checking for rl_done in -lreadline... yes
------------------------------------------------
Checking for widget libraries (provides GUI_...)
------------------------------------------------
configure: WARNING: No GUI functionality enabled
Options:
toon readline
Missing options:
gui
GUI support:
none
configure: creating ./config.status
config.status: creating Makefile
config.status: creating gvars3/config.h
2-3-2. compile 컴파일하기
%%% make
실행 결과:
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/gvars3.o src/gvars3.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI.o src/GUI.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GStringUtil.o src/GStringUtil.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/gvars2.o src/gvars2.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI_language.o src/GUI_language.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/serialize.o src/serialize.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI_none.o src/GUI_none.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI_non_readline.o src/GUI_non_readline.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/inst.o src/inst.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI_readline.o src/GUI_readline.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI_impl_readline.o src/GUI_impl_readline.cc
ar crvs libGVars3.a src/gvars3.o src/GUI.o src/GStringUtil.o src/gvars2.o src/GUI_language.o src/serialize.o src/GUI_none.o src/GUI_non_readline.o src/inst.o src/GUI_readline.o src/GUI_impl_readline.o
a - src/gvars3.o
a - src/GUI.o
a - src/GStringUtil.o
a - src/gvars2.o
a - src/GUI_language.o
a - src/serialize.o
a - src/GUI_none.o
a - src/GUI_non_readline.o
a - src/inst.o
a - src/GUI_readline.o
a - src/GUI_impl_readline.o
rm -f libGVars3.dylib libGVars3-0.dylib libGVars3-0.6.dylib
g++ -dynamiclib -o libGVars3-0.6.dylib src/gvars3.o src/GUI.o src/GStringUtil.o src/gvars2.o src/GUI_language.o src/serialize.o src/GUI_none.o src/GUI_non_readline.o src/inst.o src/GUI_readline.o src/GUI_impl_readline.o -lreadline -L/sw/lib -L/opt/local/lib -lm
ln -s libGVars3-0.6.dylib libGVars3-0.dylib
ln -s libGVars3-0.dylib libGVars3.dylib
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI_impl_headless.o src/GUI_impl_headless.cc
ar crvs libGVars3_headless.a src/gvars3.o src/GUI.o src/GStringUtil.o src/gvars2.o src/GUI_language.o src/serialize.o src/GUI_none.o src/GUI_impl_headless.o src/inst.o
a - src/gvars3.o
a - src/GUI.o
a - src/GStringUtil.o
a - src/gvars2.o
a - src/GUI_language.o
a - src/serialize.o
a - src/GUI_none.o
a - src/GUI_impl_headless.o
a - src/inst.o
rm -f libGVars3_headless.dylib libGVars3_headless-0.dylib libGVars3_headless-0.6.dylib
g++ -dynamiclib -o libGVars3_headless-0.6.dylib src/gvars3.o src/GUI.o src/GStringUtil.o src/gvars2.o src/GUI_language.o src/serialize.o src/GUI_none.o src/GUI_impl_headless.o src/inst.o -L/sw/lib -L/opt/local/lib -lm
ln -s libGVars3_headless-0.6.dylib libGVars3_headless-0.dylib
ln -s libGVars3_headless-0.dylib libGVars3_headless.dylib
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI.o src/GUI.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GStringUtil.o src/GStringUtil.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/gvars2.o src/gvars2.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI_language.o src/GUI_language.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/serialize.o src/serialize.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI_none.o src/GUI_none.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI_non_readline.o src/GUI_non_readline.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/inst.o src/inst.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI_readline.o src/GUI_readline.cc
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI_impl_readline.o src/GUI_impl_readline.cc
ar crvs libGVars3.a src/gvars3.o src/GUI.o src/GStringUtil.o src/gvars2.o src/GUI_language.o src/serialize.o src/GUI_none.o src/GUI_non_readline.o src/inst.o src/GUI_readline.o src/GUI_impl_readline.o
a - src/gvars3.o
a - src/GUI.o
a - src/GStringUtil.o
a - src/gvars2.o
a - src/GUI_language.o
a - src/serialize.o
a - src/GUI_none.o
a - src/GUI_non_readline.o
a - src/inst.o
a - src/GUI_readline.o
a - src/GUI_impl_readline.o
rm -f libGVars3.dylib libGVars3-0.dylib libGVars3-0.6.dylib
g++ -dynamiclib -o libGVars3-0.6.dylib src/gvars3.o src/GUI.o src/GStringUtil.o src/gvars2.o src/GUI_language.o src/serialize.o src/GUI_none.o src/GUI_non_readline.o src/inst.o src/GUI_readline.o src/GUI_impl_readline.o -lreadline -L/sw/lib -L/opt/local/lib -lm
ln -s libGVars3-0.6.dylib libGVars3-0.dylib
ln -s libGVars3-0.dylib libGVars3.dylib
g++ -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -D_REENTRANT -Wall -Wextra -pthread -I. -I /sw/include -I/opt/local/include -I/usr/X11R6/include -INONE/include -DGUI_HAVE_READLINE -c -o src/GUI_impl_headless.o src/GUI_impl_headless.cc
ar crvs libGVars3_headless.a src/gvars3.o src/GUI.o src/GStringUtil.o src/gvars2.o src/GUI_language.o src/serialize.o src/GUI_none.o src/GUI_impl_headless.o src/inst.o
a - src/gvars3.o
a - src/GUI.o
a - src/GStringUtil.o
a - src/gvars2.o
a - src/GUI_language.o
a - src/serialize.o
a - src/GUI_none.o
a - src/GUI_impl_headless.o
a - src/inst.o
rm -f libGVars3_headless.dylib libGVars3_headless-0.dylib libGVars3_headless-0.6.dylib
g++ -dynamiclib -o libGVars3_headless-0.6.dylib src/gvars3.o src/GUI.o src/GStringUtil.o src/gvars2.o src/GUI_language.o src/serialize.o src/GUI_none.o src/GUI_impl_headless.o src/inst.o -L/sw/lib -L/opt/local/lib -lm
ln -s libGVars3_headless-0.6.dylib libGVars3_headless-0.dylib
ln -s libGVars3_headless-0.dylib libGVars3_headless.dylib
2-3-3. install 설치하기
%%% sudo make install
mkdir -p //usr/local/lib
cp libGVars3.a libGVars3_headless.a //usr/local/lib
mkdir -p //usr/local/lib
cp libGVars3-0.6.dylib //usr/local/lib
ln -fs //usr/local/lib/libGVars3-0.6.dylib //usr/local/lib/libGVars3-0.dylib
ln -fs //usr/local/lib/libGVars3-0.dylib //usr/local/lib/libGVars3.dylib
mkdir -p //usr/local/lib
cp libGVars3_headless-0.6.dylib //usr/local/lib
ln -fs //usr/local/lib/libGVars3_headless-0.6.dylib //usr/local/lib/libGVars3_headless-0.dylib
ln -fs //usr/local/lib/libGVars3_headless-0.dylib //usr/local/lib/libGVars3_headless.dylib
mkdir -p //usr/local/include
cp -r gvars3 //usr/local/include
cp libGVars3.a libGVars3_headless.a //usr/local/lib
mkdir -p //usr/local/lib
cp libGVars3-0.6.dylib //usr/local/lib
ln -fs //usr/local/lib/libGVars3-0.6.dylib //usr/local/lib/libGVars3-0.dylib
ln -fs //usr/local/lib/libGVars3-0.dylib //usr/local/lib/libGVars3.dylib
mkdir -p //usr/local/lib
cp libGVars3_headless-0.6.dylib //usr/local/lib
ln -fs //usr/local/lib/libGVars3_headless-0.6.dylib //usr/local/lib/libGVars3_headless-0.dylib
ln -fs //usr/local/lib/libGVars3_headless-0.dylib //usr/local/lib/libGVars3_headless.dylib
mkdir -p //usr/local/include
cp -r gvars3 //usr/local/include
2-4. OS X에서의 컴파일링과 관련하여
ref. UNIX에서 컴파일하기
Porting UNIX/Linux Applications to Mac OS X: Compiling Your Code in Mac OS X
3. PTAM 컴파일
3-1. 해당 플랫폼의 빌드 파일을 PTAM source 디렉토리로 복사
내 (OS X의) 경우, PTAM/Build/OS X에 있는 모든 (두 개의) 파일 Makefile과 VideoSource_OSX.cc를 PTAM 폴더에 옮겼다.
3-2. video source 셋업
카메라에 맞는 video input file을 컴파일하도록 Makefile을 수정해 주어야 한다.
맥의 경우, (아마도 Logitech Quickcam Pro 5000 을 기준으로 하는) 하나의 소스 파일만이 존재하므로 그대로 두면 될 듯.
3-3. video source 추가
다른 비디오 소스들은 libCVD에 클래스로 만들어져 있다고 한다. 여기에 포함되어 있지 않은 경우에는 VideoSource_XYZ.cc 라는 식의 이름을 갖는 파일을 만들어서 넣어 주어야 한다.
3-4. compile
PTAM 폴더에 들어가서
%% make
실행 결과:
g++ -g -O3 main.cc -o main.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT
g++ -g -O3 VideoSource_OSX.cc -o VideoSource_OSX.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT
g++ -g -O3 GLWindow2.cc -o GLWindow2.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT
In file included from OpenGL.h:20,
from GLWindow2.cc:1:
/usr/local/include/cvd/gl_helpers.h:38:19: error: GL/gl.h: No such file or directory
/usr/local/include/cvd/gl_helpers.h:39:20: error: GL/glu.h: No such file or directory
/usr/local/include/cvd/gl_helpers.h: In function 'void CVD::glPrintErrors()':
/usr/local/include/cvd/gl_helpers.h:569: error: 'gluGetString' was not declared in this scope
make: *** [GLWindow2.o] Error 1
g++ -g -O3 VideoSource_OSX.cc -o VideoSource_OSX.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT
g++ -g -O3 GLWindow2.cc -o GLWindow2.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT
In file included from OpenGL.h:20,
from GLWindow2.cc:1:
/usr/local/include/cvd/gl_helpers.h:38:19: error: GL/gl.h: No such file or directory
/usr/local/include/cvd/gl_helpers.h:39:20: error: GL/glu.h: No such file or directory
/usr/local/include/cvd/gl_helpers.h: In function 'void CVD::glPrintErrors()':
/usr/local/include/cvd/gl_helpers.h:569: error: 'gluGetString' was not declared in this scope
make: *** [GLWindow2.o] Error 1
이 에러 메시지는 다음 링크에서 논의되고 있는 문제와 비슷한 상황인 것 같다.
http://en.allexperts.com/q/Unix-Linux-OS-1064/Compiling-OpenGL-unix-linux.htm
3-4-1. OpenGL on UNIX
PTAM이 OpenGL을 사용하고 있는데, OpenGL이 Mac에 기본으로 설치되어 있으므로 신경쓰지 않았던 부분이다. 물론 system의 public framework으로 들어가 있음을 확인할 수 있다. 그런데 UNIX 프로그램에서 접근할 수는 없는가? (인터넷에서 검색해 보아도 따로 설치할 수 있는 다운로드 링크나 방법을 찾을 수 없다.)
에러 메시지에 대한 정확한 진단 ->
philphys: 일단 OpenGL은 분명히 있을 건데 그 헤더파일과 라이브러리가 있는 곳을 지정해 주지 않아서 에러가 나는 것 같아. 보통 Makefile에 이게 지정되어 있어야 하는데 실행결과를 보니까 전혀 지정되어 있지 않네. 중간에 보면 -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ 라는 부분이 헤더 파일의 위치를 지정해 주는 부분이고 또 라이브러리는 뒤에 링크할 때 지정해 주게 되어 있는데 거기까지는 가지도 못 했네.즉, "링커가 문제가 아니라, 컴파일러 옵션에 OpenGL의 헤더파일이 있는 디렉토리를 지정해 주어야 할 것 같다"고 한다.
문제의 Makefile을 들여다보고
# DO NOT DELETE THIS LINE -- make depend depends on it.
# Edit the lines below to point to any needed include and link paths
# Or to change the compiler's optimization flags
CC = g++ -g -O3
COMPILEFLAGS = -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT
LINKFLAGS = -framework OpenGL -framework VecLib -L/MY_CUSTOM_LINK_PATH/ -lGVars3 -lcvd
OBJECTS= main.o\
VideoSource_OSX.o\
GLWindow2.o\
GLWindowMenu.o\
System.o \
ATANCamera.o\
KeyFrame.o\
MapPoint.o\
Map.o\
SmallBlurryImage.o\
ShiTomasi.o \
MapMaker.o \
Bundle.o \
PatchFinder.o\
HomographyInit.o\
Relocaliser.o\
MiniPatch.o\
MapViewer.o\
ARDriver.o\
EyeGame.o\
Tracker.o
CALIB_OBJECTS= GLWindow2.o\
GLWindowMenu.o\
VideoSource_OSX.o \
CalibImage.o \
CalibCornerPatch.o\
ATANCamera.o \
CameraCalibrator.o
All: PTAM CameraCalibrator
PTAM:$(OBJECTS)
$(CC) -o PTAM $(OBJECTS) $(LINKFLAGS)
/Developer/Tools/Rez OSX_resource_file.r -o PTAM
CameraCalibrator:$(CALIB_OBJECTS)
$(CC) -o CameraCalibrator $(CALIB_OBJECTS) $(LINKFLAGS)
/Developer/Tools/Rez OSX_resource_file.r -o CameraCalibrator
%.o: %.cc
$(CC) $< -o $@ -c $(COMPILEFLAGS)
clean:
rm *.o
depend:
rm dependecies; touch dependencies
makedepend -fdependencies $(INCLUDEFLAGS) $(MOREINCS) *.cc *.h
-include dependencies
# Edit the lines below to point to any needed include and link paths
# Or to change the compiler's optimization flags
CC = g++ -g -O3
COMPILEFLAGS = -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT
LINKFLAGS = -framework OpenGL -framework VecLib -L/MY_CUSTOM_LINK_PATH/ -lGVars3 -lcvd
OBJECTS= main.o\
VideoSource_OSX.o\
GLWindow2.o\
GLWindowMenu.o\
System.o \
ATANCamera.o\
KeyFrame.o\
MapPoint.o\
Map.o\
SmallBlurryImage.o\
ShiTomasi.o \
MapMaker.o \
Bundle.o \
PatchFinder.o\
HomographyInit.o\
Relocaliser.o\
MiniPatch.o\
MapViewer.o\
ARDriver.o\
EyeGame.o\
Tracker.o
CALIB_OBJECTS= GLWindow2.o\
GLWindowMenu.o\
VideoSource_OSX.o \
CalibImage.o \
CalibCornerPatch.o\
ATANCamera.o \
CameraCalibrator.o
All: PTAM CameraCalibrator
PTAM:$(OBJECTS)
$(CC) -o PTAM $(OBJECTS) $(LINKFLAGS)
/Developer/Tools/Rez OSX_resource_file.r -o PTAM
CameraCalibrator:$(CALIB_OBJECTS)
$(CC) -o CameraCalibrator $(CALIB_OBJECTS) $(LINKFLAGS)
/Developer/Tools/Rez OSX_resource_file.r -o CameraCalibrator
%.o: %.cc
$(CC) $< -o $@ -c $(COMPILEFLAGS)
clean:
rm *.o
depend:
rm dependecies; touch dependencies
makedepend -fdependencies $(INCLUDEFLAGS) $(MOREINCS) *.cc *.h
-include dependencies
(다음은 philphys 인용)
파란색 부분 - 각 소스코드를 컴파일한 다음 컴파일된 오브젝트 코드를 실행파일로 링크하는 부분. 여기서는 $(LINKFLAGS)에 링커 프로그램에 전달되는 옵션이 들어간다.
초록색 부분 - 컴파일할 오브젝트 코드의 리스트
분홍색 부분 - CC는 컴파일러 프로그램과 기본 옵션. COMPILEFLAGS는 컴파일러에 전달하는 옵션들, 여기에 헤더 파일의 위치를 정할 수 있다. LINKFLAGS는 컴파일된 오브젝트 코드를 실행파일로 링크하는 링커에 들어가는 옵션. 여기에 라이브러리의 위치와 사용할 라이브러리를 지정해 준다. 라이브러리의 위치는 -L 옵션으로, 구체적인 라이브러리 이름은 -l 옵션으로.
maetel: 사실 프레임웍 안에 gl.h 파일이 있는 위치는 다음과 같다.
/System/Library/Frameworks/OpenGL.framework/Versions/A/Headers
philphys: "근데 코드에서는 그 헤더를 "GL/gl.h"로 찾는다는 게 문제. 이건 프레임웍 방식이 아닌 고전적인 유닉스 Xwindows의 OpenGL 방식이다. 즉 방금 보인 gl.h, glu.h 등이 있는 /usr/X11R6/include 를 COMPILERFLAGS에 -I 옵션으로 넣어 줘야 하는 게 아닐까."
Makefile을 다음과 같이 수정하고 (보라색 부분 추가)
COMPILEFLAGS = -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
philphys: /usr/X11R6/include 밑에 GL 폴더가 있고 거기에 필요한 헤더파일들이 모두 들어 있다. 그래서 코드에선 "GL/gl.h" 하는 식으로 explicit하게 GL 폴더를 찾게 된다.
그러고 보면 아래와 같은 설명이 있었던 것이다.
Since the Linux code compiles directly against the nVidia driver's GL headers, use of a different GL driver may require some modifications to the code.
다시 컴파일 하니,
실행 결과:
g++ -g -O3 GLWindow2.cc -o GLWindow2.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 GLWindowMenu.cc -o GLWindowMenu.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 System.cc -o System.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 ATANCamera.cc -o ATANCamera.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 KeyFrame.cc -o KeyFrame.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 MapPoint.cc -o MapPoint.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 Map.cc -o Map.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 SmallBlurryImage.cc -o SmallBlurryImage.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 ShiTomasi.cc -o ShiTomasi.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 MapMaker.cc -o MapMaker.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 Bundle.cc -o Bundle.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 PatchFinder.cc -o PatchFinder.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 HomographyInit.cc -o HomographyInit.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 Relocaliser.cc -o Relocaliser.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 MiniPatch.cc -o MiniPatch.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 MapViewer.cc -o MapViewer.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 ARDriver.cc -o ARDriver.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 EyeGame.cc -o EyeGame.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 Tracker.cc -o Tracker.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 -o PTAM main.o VideoSource_OSX.o GLWindow2.o GLWindowMenu.o System.o ATANCamera.o KeyFrame.o MapPoint.o Map.o SmallBlurryImage.o ShiTomasi.o MapMaker.o Bundle.o PatchFinder.o HomographyInit.o Relocaliser.o MiniPatch.o MapViewer.o ARDriver.o EyeGame.o Tracker.o -framework OpenGL -framework VecLib -L/MY_CUSTOM_LINK_PATH/ -lGVars3 -lcvd
/Developer/Tools/Rez OSX_resource_file.r -o PTAM
g++ -g -O3 CalibImage.cc -o CalibImage.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 CalibCornerPatch.cc -o CalibCornerPatch.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 CameraCalibrator.cc -o CameraCalibrator.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 -o CameraCalibrator GLWindow2.o GLWindowMenu.o VideoSource_OSX.o CalibImage.o CalibCornerPatch.o ATANCamera.o CameraCalibrator.o -framework OpenGL -framework VecLib -L/MY_CUSTOM_LINK_PATH/ -lGVars3 -lcvd
/Developer/Tools/Rez OSX_resource_file.r -o CameraCalibrator
g++ -g -O3 GLWindowMenu.cc -o GLWindowMenu.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 System.cc -o System.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 ATANCamera.cc -o ATANCamera.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 KeyFrame.cc -o KeyFrame.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 MapPoint.cc -o MapPoint.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 Map.cc -o Map.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 SmallBlurryImage.cc -o SmallBlurryImage.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 ShiTomasi.cc -o ShiTomasi.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 MapMaker.cc -o MapMaker.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 Bundle.cc -o Bundle.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 PatchFinder.cc -o PatchFinder.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 HomographyInit.cc -o HomographyInit.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 Relocaliser.cc -o Relocaliser.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 MiniPatch.cc -o MiniPatch.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 MapViewer.cc -o MapViewer.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 ARDriver.cc -o ARDriver.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 EyeGame.cc -o EyeGame.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 Tracker.cc -o Tracker.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 -o PTAM main.o VideoSource_OSX.o GLWindow2.o GLWindowMenu.o System.o ATANCamera.o KeyFrame.o MapPoint.o Map.o SmallBlurryImage.o ShiTomasi.o MapMaker.o Bundle.o PatchFinder.o HomographyInit.o Relocaliser.o MiniPatch.o MapViewer.o ARDriver.o EyeGame.o Tracker.o -framework OpenGL -framework VecLib -L/MY_CUSTOM_LINK_PATH/ -lGVars3 -lcvd
/Developer/Tools/Rez OSX_resource_file.r -o PTAM
g++ -g -O3 CalibImage.cc -o CalibImage.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 CalibCornerPatch.cc -o CalibCornerPatch.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 CameraCalibrator.cc -o CameraCalibrator.o -c -I /MY_CUSTOM_INCLUDE_PATH/ -D_OSX -D_REENTRANT -I/usr/X11R6/include/
g++ -g -O3 -o CameraCalibrator GLWindow2.o GLWindowMenu.o VideoSource_OSX.o CalibImage.o CalibCornerPatch.o ATANCamera.o CameraCalibrator.o -framework OpenGL -framework VecLib -L/MY_CUSTOM_LINK_PATH/ -lGVars3 -lcvd
/Developer/Tools/Rez OSX_resource_file.r -o CameraCalibrator
설치 완료!
두 실행파일 PTAM과 CameraCalibrator이 생성되었다.
3-5. X11R6에 대하여
X11R6 = Xwindow Verion 11 Release 6
Xwindow
X.org
4. camera calibration
CameraCalibrator 파일을 실행시켜 카메라 캘리브레이션을 시도했더니 GUI 창이 뜨는데 연결된 웹캠(Logitech QuickCam Pro 4000)으로부터 입력을 받지 못 한다.
4-0. 증상
CameraCalibrator 실행파일을 열면, 다음과 같은 터미널 창이 새로 열린다.
Last login: Fri Aug 7 01:14:05 on ttys001
%% /Users/lym/PTAM/CameraCalibrator ; exit;
Welcome to CameraCalibrator
--------------------------------------
Parallel tracking and mapping for Small AR workspaces
Copyright (C) Isis Innovation Limited 2008
Parsing calibrator_settings.cfg ....
! GUI_impl::Loadfile: Failed to load script file "calibrator_settings.cfg".
VideoSource_OSX: Creating QTBuffer....
IMPORTANT
This will open a quicktime settings planel.
You should use this settings dialog to turn the camera's
sharpness to a minimum, or at least so small that no sharpening
artefacts appear! In-camera sharpening will seriously degrade the
performance of both the camera calibrator and the tracking system.
>
%% /Users/lym/PTAM/CameraCalibrator ; exit;
Welcome to CameraCalibrator
--------------------------------------
Parallel tracking and mapping for Small AR workspaces
Copyright (C) Isis Innovation Limited 2008
Parsing calibrator_settings.cfg ....
! GUI_impl::Loadfile: Failed to load script file "calibrator_settings.cfg".
VideoSource_OSX: Creating QTBuffer....
IMPORTANT
This will open a quicktime settings planel.
You should use this settings dialog to turn the camera's
sharpness to a minimum, or at least so small that no sharpening
artefacts appear! In-camera sharpening will seriously degrade the
performance of both the camera calibrator and the tracking system.
>
그리고 Video란 이름의 GUI 창이 열리는데, 이때 아무런 설정을 바꾸지 않고 그대로 OK를 누르면 위의 터미널 창에 다음과 같은 메시지가 이어지면서 자동 종료된다.
.. created QTBuffer of size [640 480]
2009-08-07 01:20:57.231 CameraCalibrator[40836:10b] ***_NSAutoreleaseNoPool(): Object 0xf70e2c0 of class NSThread autoreleasedwith no pool in place - just leaking
Stack: (0x96827f0f 0x96734442 0x9673a1b4 0xbc2db7 0xbc7e9a 0xbc69d30xbcacbd 0xbca130 0x964879c9 0x90f8dfb8 0x90e69618 0x90e699840x964879c9 0x90f9037c 0x90e7249c 0x90e69984 0x964879c9 0x90f8ec800x90e55e05 0x90e5acd5 0x90e5530f 0x964879c9 0x94179eb9 0x282b48 0xd9f40xd6a6 0x2f16b 0x2fea4 0x26b6)
! Code for converting from format "Raw RGB data"
not implemented yet, check VideoSource_OSX.cc.
logout
[Process completed]
2009-08-07 01:20:57.231 CameraCalibrator[40836:10b] ***_NSAutoreleaseNoPool(): Object 0xf70e2c0 of class NSThread autoreleasedwith no pool in place - just leaking
Stack: (0x96827f0f 0x96734442 0x9673a1b4 0xbc2db7 0xbc7e9a 0xbc69d30xbcacbd 0xbca130 0x964879c9 0x90f8dfb8 0x90e69618 0x90e699840x964879c9 0x90f9037c 0x90e7249c 0x90e69984 0x964879c9 0x90f8ec800x90e55e05 0x90e5acd5 0x90e5530f 0x964879c9 0x94179eb9 0x282b48 0xd9f40xd6a6 0x2f16b 0x2fea4 0x26b6)
! Code for converting from format "Raw RGB data"
not implemented yet, check VideoSource_OSX.cc.
logout
[Process completed]
그러므로 3-3의 문제 -- set up video source (비디오 소스 셋업) --로 돌아가야 한다.
즉, VideoSource_OSX.cc 파일을 수정해서 다시 컴파일한 후 실행해야 한다.
Other video source classes are available with libCVD. Finally, if a custom video source not supported by libCVD is required, the code for it will have to be put into some VideoSource_XYZ.cc file (the interface for this file is very simple.)
삽질...
터미널에서 calibrator_settings.cfg 파일을 로드하지 못 했다고 하기에, 그 파일을 찾아보았다.
%% find . -name "calibrator_settings.cfg" -print
./calibrator_settings.cfg
알고 보니 ./는 현재 디렉토리를 말하나 보다. PTAM 폴더 밑에 바로 있다. 왜 못 봤을까...
열어 보니 다음과 같다.
// This file is parsed by the CameraCalibrator executable
// Put any custom gvars settings you want in here
// For example: to increase the camera calibrator's blur parameter,
// uncomment the following line
// CameraCalibrator.BlurSigma=2.0
// Put any custom gvars settings you want in here
// For example: to increase the camera calibrator's blur parameter,
// uncomment the following line
// CameraCalibrator.BlurSigma=2.0
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Context-free_grammar
모두 주석 처리되어 있는 파일이다. 당장 해결해야 하는 에러는 아닌가 보다.
4-1. VideoSource_OSX.cc 파일 수정
4-1-0. 원래의 VideoSource_OSX.cc 파일
소스 코드:
// Copyright 2008 Isis Innovation Limited
#include "VideoSource.h"
#include <cvd/OSX/qtbuffer.h>
#include <cvd/colourspace_convert.h>
#include <cvd/colourspaces.h>
using namespace CVD;
using namespace std;
VideoSource::VideoSource()
{
cout << " VideoSource_OSX: Creating QTBuffer...." << endl;
cout << " IMPORTANT " << endl;
cout << " This will open a quicktime settings planel. " << endl
<< " You should use this settings dialog to turn the camera's " << endl
<< " sharpness to a minimum, or at least so small that no sharpening " << endl
<< " artefacts appear! In-camera sharpening will seriously degrade the " << endl
<< " performance of both the camera calibrator and the tracking system. " << endl;
QTBuffer<yuv422>* pvb;
try
{
pvb= new QTBuffer<yuv422>(ImageRef(640,480), 0, true);
}
catch (CVD::Exceptions::All a)
{
cerr << " Error creating QTBuffer; expection: " << a.what << endl;
exit(1);
}
mptr = pvb;
mirSize = pvb->size();
cout << " .. created QTBuffer of size " << mirSize << endl;
};
ImageRef VideoSource::Size()
{
return mirSize;
};
void VideoSource::GetAndFillFrameBWandRGB(Image<byte> &imBW, Image<Rgb<byte> > &imRGB)
{
QTBuffer<yuv422>* pvb = (QTBuffer<yuv422>*) mptr;
while(!pvb->frame_pending())
usleep(2000);
VideoFrame<yuv422> *pVidFrame = pvb->get_frame();
if(pvb->get_frame_format_string().find("yuyv") != string::npos)
{
convert_image(*pVidFrame, imBW);
convert_image(*pVidFrame, imRGB);
}
else if(pvb->get_frame_format_string().find("uyvy") != string::npos)
{
convert_image(*((VideoFrame<vuy422>*)pVidFrame), imBW);
convert_image(*((VideoFrame<vuy422>*)pVidFrame), imRGB);
}
else
{
cout << "! Code for converting from format \"" << pvb->get_frame_format_string()
<< "\"" << endl << " not implemented yet, check VideoSource_OSX.cc. " << endl;
exit(1);
}
pvb->put_frame(pVidFrame);
}
#include "VideoSource.h"
#include <cvd/OSX/qtbuffer.h>
#include <cvd/colourspace_convert.h>
#include <cvd/colourspaces.h>
using namespace CVD;
using namespace std;
VideoSource::VideoSource()
{
cout << " VideoSource_OSX: Creating QTBuffer...." << endl;
cout << " IMPORTANT " << endl;
cout << " This will open a quicktime settings planel. " << endl
<< " You should use this settings dialog to turn the camera's " << endl
<< " sharpness to a minimum, or at least so small that no sharpening " << endl
<< " artefacts appear! In-camera sharpening will seriously degrade the " << endl
<< " performance of both the camera calibrator and the tracking system. " << endl;
QTBuffer<yuv422>* pvb;
try
{
pvb= new QTBuffer<yuv422>(ImageRef(640,480), 0, true);
}
catch (CVD::Exceptions::All a)
{
cerr << " Error creating QTBuffer; expection: " << a.what << endl;
exit(1);
}
mptr = pvb;
mirSize = pvb->size();
cout << " .. created QTBuffer of size " << mirSize << endl;
};
ImageRef VideoSource::Size()
{
return mirSize;
};
void VideoSource::GetAndFillFrameBWandRGB(Image<byte> &imBW, Image<Rgb<byte> > &imRGB)
{
QTBuffer<yuv422>* pvb = (QTBuffer<yuv422>*) mptr;
while(!pvb->frame_pending())
usleep(2000);
VideoFrame<yuv422> *pVidFrame = pvb->get_frame();
if(pvb->get_frame_format_string().find("yuyv") != string::npos)
{
convert_image(*pVidFrame, imBW);
convert_image(*pVidFrame, imRGB);
}
else if(pvb->get_frame_format_string().find("uyvy") != string::npos)
{
convert_image(*((VideoFrame<vuy422>*)pVidFrame), imBW);
convert_image(*((VideoFrame<vuy422>*)pVidFrame), imRGB);
}
else
{
cout << "! Code for converting from format \"" << pvb->get_frame_format_string()
<< "\"" << endl << " not implemented yet, check VideoSource_OSX.cc. " << endl;
exit(1);
}
pvb->put_frame(pVidFrame);
}
오렌지 색 부분의 string이 출력되었으니, GetAndFillFrameBWandRGB 함수 아래 조건문에서 걸리지 않고 있음을 알 수 있다.
4-1-1. "Raw" 추가
그리고 콘솔에 다음 메시지가 나왔으므로
! Code for converting from format "Raw RGB data"
코드에서 else if(pvb->get_frame_format_string().find("uyvy") != string::npos) { } 아래 58줄에
다음과 같이 조건문을 하나 추가해 주었다.
else if(pvb->get_frame_format_string().find("Raw") != string::npos)
{
convert_image(*((VideoFrame<vuy422>*)pVidFrame), imBW);
convert_image(*((VideoFrame<vuy422>*)pVidFrame), imRGB);
}
{
convert_image(*((VideoFrame<vuy422>*)pVidFrame), imBW);
convert_image(*((VideoFrame<vuy422>*)pVidFrame), imRGB);
}
이제 입력이 들어오기 시작한다! (thank kyu!)
 |
 |
그러나 위에서 보듯 size가 맞지 않고 frame이 겹치는 등 넘어갈 수 없는 문제가 있다. (오른쪽 이미지는 같은 상황에서의 비교를 위해 맥용 드라이버 macam에서의 입력을 캡쳐한 것.)
터미널에서의 결과:
%% /Users/lym/PTAM/CameraCalibrator ; exit;
Welcome to CameraCalibrator
--------------------------------------
Parallel tracking and mapping for Small AR workspaces
Copyright (C) Isis Innovation Limited 2008
Parsing calibrator_settings.cfg ....
! GUI_impl::Loadfile: Failed to load script file "calibrator_settings.cfg".
VideoSource_OSX: Creating QTBuffer....
IMPORTANT
This will open a quicktime settings planel.
You should use this settings dialog to turn the camera's
sharpness to a minimum, or at least so small that no sharpening
artefacts appear! In-camera sharpening will seriously degrade the
performance of both the camera calibrator and the tracking system.
> .. created QTBuffer of size [640 480]
2009-08-12 23:10:38.309 CameraCalibrator[5110:10b] *** _NSAutoreleaseNoPool(): Object 0xf8054e0 of class NSThread autoreleased with no pool in place - just leaking
Stack: (0x96670f4f 0x9657d432 0x965831a4 0xc17db7 0xc1ce9a 0xc1b9d3 0xc1fcbd 0xc1f130 0x924b09c9 0x958e8fb8 0x957c4618 0x957c4984 0x924b09c9 0x958eb37c 0x957cd49c 0x957c4984 0x924b09c9 0x958e9c80 0x957b0e05 0x957b5cd5 0x957b030f 0x924b09c9 0x90bd4eb9 0x282b48 0xd9e4 0xd5a6 0x2f15b 0x2fe94 0x25b6)
Welcome to CameraCalibrator
--------------------------------------
Parallel tracking and mapping for Small AR workspaces
Copyright (C) Isis Innovation Limited 2008
Parsing calibrator_settings.cfg ....
! GUI_impl::Loadfile: Failed to load script file "calibrator_settings.cfg".
VideoSource_OSX: Creating QTBuffer....
IMPORTANT
This will open a quicktime settings planel.
You should use this settings dialog to turn the camera's
sharpness to a minimum, or at least so small that no sharpening
artefacts appear! In-camera sharpening will seriously degrade the
performance of both the camera calibrator and the tracking system.
> .. created QTBuffer of size [640 480]
2009-08-12 23:10:38.309 CameraCalibrator[5110:10b] *** _NSAutoreleaseNoPool(): Object 0xf8054e0 of class NSThread autoreleased with no pool in place - just leaking
Stack: (0x96670f4f 0x9657d432 0x965831a4 0xc17db7 0xc1ce9a 0xc1b9d3 0xc1fcbd 0xc1f130 0x924b09c9 0x958e8fb8 0x957c4618 0x957c4984 0x924b09c9 0x958eb37c 0x957cd49c 0x957c4984 0x924b09c9 0x958e9c80 0x957b0e05 0x957b5cd5 0x957b030f 0x924b09c9 0x90bd4eb9 0x282b48 0xd9e4 0xd5a6 0x2f15b 0x2fe94 0x25b6)
4-1-2. YUV format 확인
Logitech QuickCam Pro 4000는 YUV420P라는 글을 어디선가 보고, 코드의 yuv422 부분을 yuv420p로 바꾸었으나 증상은 그대로이다.
ref. YUV422 또는 YUV411 또는 YUV420P
http://ozviz.wasp.uwa.edu.au/~pbourke/dataformats/yuv/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YUV
skype forum: There is another problem here with Xgl unfortunately, as it isn'tsupporting the YUV420P (I420) overlay colour/pixel format either. Soeven if the camera captures successfully (which looks okay on thosesettings), then you still won't see anything.
 |
 |
왼쪽: macam에서 캡쳐한 이미지 / 오른쪽: PTAM CameraCalibrator에서 보여지는 이미지
Logitech QuickCam Pro 4000
 |
 |
왼쪽: macam에서 캡쳐한 이미지 / 오른쪽: PTAM CameraCalibrator에서 보여지는 이미지
Logitech QuickCam® Communicate STX™
Xgl이란 것과 관련이 있나... 일주일에 걸쳐 무수한 삽질을 거듭하다가...
ref. http://developer.apple.com/quicktime/icefloe/dispatch020.html
코드의 yuv422 부분을 그대로 두고, 추가했던 "Raw" 경우의 조건문 안에서만 분홍색 부분처럼 바꾸니
else if(pvb->get_frame_format_string().find("Raw") != string::npos)
{
convert_image(*((VideoFrame<Rgb<byte> >*)pVidFrame), imBW);
convert_image(*((VideoFrame<Rgb<byte> >*)pVidFrame), imRGB);
}
{
convert_image(*((VideoFrame<Rgb<byte> >*)pVidFrame), imBW);
convert_image(*((VideoFrame<Rgb<byte> >*)pVidFrame), imRGB);
}
된다! ㅜㅜ (thank jini!)
 |
 |
왼쪽: Logitech QuickCam® Communicate STX™ / 오른쪽: Logitech QuickCam Pro 4000
4-1-3. qtbuffer.h
cam_type<Rgb<byte> >
ref.
http://developer.apple.com/samplecode/ElectricImageComponent/listing2.html
수정한 VideoSource 파일
터미널 창:
Welcome to CameraCalibrator
--------------------------------------
Parallel tracking and mapping for Small AR workspaces
Copyright (C) Isis Innovation Limited 2008
Parsing calibrator_settings.cfg ....
VideoSource_OSX: Creating QTBuffer....
IMPORTANT
This will open a quicktime settings planel.
You should use this settings dialog to turn the camera's
sharpness to a minimum, or at least so small that no sharpening
artefacts appear! In-camera sharpening will seriously degrade the
performance of both the camera calibrator and the tracking system.
> .. created QTBuffer of size [640 480]
2009-08-13 04:02:50.464 CameraCalibrator[6251:10b] *** _NSAutoreleaseNoPool(): Object 0x9df180 of class NSThread autoreleased with no pool in place - just leaking
Stack: (0x96670f4f 0x9657d432 0x965831a4 0xbc2db7 0xbc7e9a 0xbc69d3 0xbcacbd 0xbca130 0x924b09c9 0x958e8fb8 0x957c4618 0x957c4984 0x924b09c9 0x958eb37c 0x957cd49c 0x957c4984 0x924b09c9 0x958e9c80 0x957b0e05 0x957b5cd5 0x957b030f 0x924b09c9 0x90bd4eb9 0x282b48 0xd414 0xcfd6 0x2f06b 0x2fda4)
--------------------------------------
Parallel tracking and mapping for Small AR workspaces
Copyright (C) Isis Innovation Limited 2008
Parsing calibrator_settings.cfg ....
VideoSource_OSX: Creating QTBuffer....
IMPORTANT
This will open a quicktime settings planel.
You should use this settings dialog to turn the camera's
sharpness to a minimum, or at least so small that no sharpening
artefacts appear! In-camera sharpening will seriously degrade the
performance of both the camera calibrator and the tracking system.
> .. created QTBuffer of size [640 480]
2009-08-13 04:02:50.464 CameraCalibrator[6251:10b] *** _NSAutoreleaseNoPool(): Object 0x9df180 of class NSThread autoreleased with no pool in place - just leaking
Stack: (0x96670f4f 0x9657d432 0x965831a4 0xbc2db7 0xbc7e9a 0xbc69d3 0xbcacbd 0xbca130 0x924b09c9 0x958e8fb8 0x957c4618 0x957c4984 0x924b09c9 0x958eb37c 0x957cd49c 0x957c4984 0x924b09c9 0x958e9c80 0x957b0e05 0x957b5cd5 0x957b030f 0x924b09c9 0x90bd4eb9 0x282b48 0xd414 0xcfd6 0x2f06b 0x2fda4)
4-2. Camera Calibrator 실행
Camera calib is [ 1.51994 2.03006 0.499577 0.536311 -0.0005 ]
Saving camera calib to camera.cfg...
.. saved.
Saving camera calib to camera.cfg...
.. saved.
5. PTAM 실행
Welcome to PTAM
---------------
Parallel tracking and mapping for Small AR workspaces
Copyright (C) Isis Innovation Limited 2008
Parsing settings.cfg ....
VideoSource_OSX: Creating QTBuffer....
IMPORTANT
This will open a quicktime settings planel.
You should use this settings dialog to turn the camera's
sharpness to a minimum, or at least so small that no sharpening
artefacts appear! In-camera sharpening will seriously degrade the
performance of both the camera calibrator and the tracking system.
> .. created QTBuffer of size [640 480]
2009-08-13 20:17:54.162 ptam[1374:10b] *** _NSAutoreleaseNoPool(): Object 0x8f5850 of class NSThread autoreleased with no pool in place - just leaking
Stack: (0x96670f4f 0x9657d432 0x965831a4 0xbb9db7 0xbbee9a 0xbbd9d3 0xbc1cbd 0xbc1130 0x924b09c9 0x958e8fb8 0x957c4618 0x957c4984 0x924b09c9 0x958eb37c 0x957cd49c 0x957c4984 0x924b09c9 0x958e9c80 0x957b0e05 0x957b5cd5 0x957b030f 0x924b09c9 0x90bd4eb9 0x282b48 0x6504 0x60a6 0x11af2 0x28da 0x2766)
ARDriver: Creating FBO... .. created FBO.
MapMaker: made initial map with 135 points.
MapMaker: made initial map with 227 points.
---------------
Parallel tracking and mapping for Small AR workspaces
Copyright (C) Isis Innovation Limited 2008
Parsing settings.cfg ....
VideoSource_OSX: Creating QTBuffer....
IMPORTANT
This will open a quicktime settings planel.
You should use this settings dialog to turn the camera's
sharpness to a minimum, or at least so small that no sharpening
artefacts appear! In-camera sharpening will seriously degrade the
performance of both the camera calibrator and the tracking system.
> .. created QTBuffer of size [640 480]
2009-08-13 20:17:54.162 ptam[1374:10b] *** _NSAutoreleaseNoPool(): Object 0x8f5850 of class NSThread autoreleased with no pool in place - just leaking
Stack: (0x96670f4f 0x9657d432 0x965831a4 0xbb9db7 0xbbee9a 0xbbd9d3 0xbc1cbd 0xbc1130 0x924b09c9 0x958e8fb8 0x957c4618 0x957c4984 0x924b09c9 0x958eb37c 0x957cd49c 0x957c4984 0x924b09c9 0x958e9c80 0x957b0e05 0x957b5cd5 0x957b030f 0x924b09c9 0x90bd4eb9 0x282b48 0x6504 0x60a6 0x11af2 0x28da 0x2766)
ARDriver: Creating FBO... .. created FBO.
MapMaker: made initial map with 135 points.
MapMaker: made initial map with 227 points.
The software was developed with a Unibrain Fire-i colour camera, using a 2.1mm M12 (board-mount) wide-angle lens. It also runs well with a Logitech Quickcam Pro 5000 camera, modified to use the same 2.1mm M12 lens.
iSight를 Netmate 1394B 9P Bilingual to 6P 케이블로 MacMini에 연결하여 해 보니 더 잘 된다.
CameraCalibrator를 실행하면 뜨는 GUI 창에서 다음과 같이 기본 설정이 적용되고,
Source: iSight
Compression type: Component Video - CCIR-601 uyvy
Compression type: Component Video - CCIR-601 uyvy
rms error 0.3 이하로 깔끔하게 수렴된 카메라 파라미터의 계산값이 다음과 같은 식으로 나올 때,
Camera calib is [ 1.22033 1.62577 0.489375 0.641251 0.544352 ]
PTAM을 실행하면 위의 Logitech QuickCam 두 기종보다는 features를 보다 잘 잡는다. (아직은 많이 부족하지만...)
Welcome to PTAM
---------------
Parallel tracking and mapping for Small AR workspaces
Copyright (C) Isis Innovation Limited 2008
Parsing settings.cfg ....
VideoSource_OSX: Creating QTBuffer....
IMPORTANT
This will open a quicktime settings planel.
You should use this settings dialog to turn the camera's
sharpness to a minimum, or at least so small that no sharpening
artefacts appear! In-camera sharpening will seriously degrade the
performance of both the camera calibrator and the tracking system.
> .. created QTBuffer of size [640 480]
ARDriver: Creating FBO... .. created FBO.
MapMaker: made initial map with 242 points.
MapMaker: made initial map with 259 points.
MapMaker: made initial map with 323 points.
MapMaker: made initial map with 626 points.
---------------
Parallel tracking and mapping for Small AR workspaces
Copyright (C) Isis Innovation Limited 2008
Parsing settings.cfg ....
VideoSource_OSX: Creating QTBuffer....
IMPORTANT
This will open a quicktime settings planel.
You should use this settings dialog to turn the camera's
sharpness to a minimum, or at least so small that no sharpening
artefacts appear! In-camera sharpening will seriously degrade the
performance of both the camera calibrator and the tracking system.
> .. created QTBuffer of size [640 480]
ARDriver: Creating FBO... .. created FBO.
MapMaker: made initial map with 242 points.
MapMaker: made initial map with 259 points.
MapMaker: made initial map with 323 points.
MapMaker: made initial map with 626 points.
'Computer Vision' 카테고리의 다른 글
| UNIX references (0) | 2009.08.17 |
|---|---|
| PTAM to be dissected on OS X (0) | 2009.08.17 |
| SLAM related generally (0) | 2009.08.04 |
| Kalman Filter (0) | 2009.07.30 |
| OpenCV 1.0 설치 on Mac OS X (0) | 2009.07.27 |
posted by maetel

 VideoSource_OSX.cc
VideoSource_OSX.cc


 williams_etal_iccv2007.pdf
williams_etal_iccv2007.pdf






 Ehnes, J., Hirota, K., and Hirose, M. 2004.
Ehnes, J., Hirota, K., and Hirose, M. 2004.  lights.txt
lights.txt







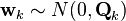


 ) equals a constant matrix (denoted
) equals a constant matrix (denoted  ) multiplied by
) multiplied by 
